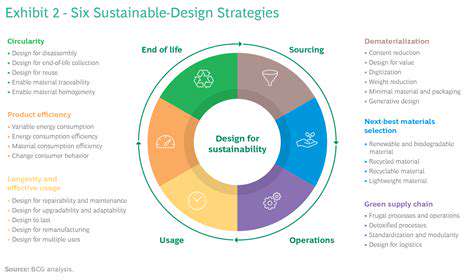
Understanding the Root Causes of Waste
Waste generation isn't a monolithic problem; it stems from various factors deeply intertwined with our daily activities and production processes. Examining the root causes, from overconsumption and inefficient packaging to improper disposal and inadequate recycling infrastructure, is crucial for developing effective waste reduction strategies. Identifying these underlying issues allows for a more targeted and holistic approach, moving beyond superficial solutions and addressing the core problems that drive waste.
A crucial component of this understanding is recognizing the interconnectedness of different sectors. Industrial waste, for example, is often linked to consumer demands and packaging choices. By analyzing these interdependencies, we can develop solutions that address waste at multiple points in the supply chain, rather than focusing solely on individual actions.
Implementing Practical Waste Reduction Strategies
Practical strategies for waste reduction encompass a wide range of approaches, from individual actions to large-scale systemic changes. Adopting reusable shopping bags and water bottles, composting food scraps, and choosing products with minimal packaging are simple yet impactful individual actions. At a broader level, companies can implement sustainable packaging designs, optimize production processes to minimize material use, and adopt circular economy models.
Implementing these strategies requires a multi-faceted approach, integrating technological advancements, policy changes, and consumer education. For instance, incentivizing the use of reusable containers through deposit-refund schemes or providing financial incentives for businesses to adopt sustainable practices can significantly encourage widespread adoption.
Promoting Sustainable Consumption Patterns
Shifting from a linear take-make-dispose model to a circular economy necessitates a fundamental change in consumption patterns. Encouraging consumers to prioritize durability, repairability, and reuse over disposability is essential. This involves educating consumers about the environmental impact of their choices and providing them with accessible alternatives, such as repair services and secondhand markets. A significant component of this shift includes promoting a culture of mindful consumption, where individuals are aware of the environmental footprint of their purchases and actively seek out sustainable options.
Engaging Diverse Stakeholders for Systemic Change
Addressing waste reduction effectively requires collaboration and engagement from various stakeholders, including individuals, businesses, governments, and non-profit organizations. Creating platforms for dialogue and knowledge sharing allows for the exchange of best practices and the development of innovative solutions. Government policies, such as extended producer responsibility schemes and tax incentives for sustainable practices, can play a critical role in driving systemic change. Furthermore, fostering partnerships between businesses and communities can facilitate the implementation of impactful waste reduction initiatives.
Ultimately, a holistic approach demands a collective commitment from all stakeholders. By fostering collaboration, knowledge sharing, and a shared vision for a sustainable future, we can create a more effective and lasting impact on waste reduction.
Implementing Closed-Loop Recycling Systems for Maximum Resource Recovery

Understanding the Closed-Loop System
Closed-loop recycling systems represent a significant advancement in waste management, aiming to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource recovery. These systems are designed to capture and reuse materials from the end of one product's life cycle, effectively transforming waste into valuable resources for the creation of new products. This approach reduces the need for virgin materials, conserving natural resources and lowering the overall environmental footprint of production.
A crucial component of closed-loop systems is the ability to consistently collect and process materials in a way that ensures high-quality end products. This requires sophisticated sorting and processing technologies to separate different materials, and to ensure that contaminants are effectively removed. The emphasis is on creating a continuous feedback loop, where the recycled materials are directly incorporated into new production processes.
Material Selection and Processing
The success of closed-loop recycling hinges on careful material selection. Certain materials, like plastics, are particularly challenging due to the wide variety of compositions and contamination levels. Developing effective sorting methods and ensuring consistent quality standards for these materials are critical to the viability of closed-loop systems.
Advanced processing techniques play a vital role in transforming collected materials into usable feedstock. These techniques often involve specialized equipment and processes to achieve high purity and consistency. The goal is to create a material stream that is readily incorporated into the manufacturing process of new products, minimizing the need for additional processing steps.
Economic Incentives and Policy Support
Implementing closed-loop recycling systems requires a multifaceted approach that extends beyond technological advancements. Strong economic incentives and supportive policies are essential for driving participation and encouraging the development of closed-loop infrastructure.
Governments can play a vital role in fostering this transition by creating favorable regulations and tax incentives that encourage companies to adopt closed-loop systems. These policies can help to offset the initial investment costs and create a more favorable market for recycled materials. This, in turn, encourages wider adoption throughout the economy.
Consumer Awareness and Engagement
Consumer awareness and engagement are key to the success of any closed-loop recycling program. Educating consumers about the importance of proper material separation and responsible disposal habits can significantly impact the quality and quantity of materials collected for recycling.
Clear communication about the benefits of closed-loop recycling and the specific materials accepted by the system is essential. Engaging consumers in the process fosters a sense of shared responsibility and incentivizes participation. Ultimately, a well-informed and engaged consumer base is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the closed-loop system.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Continuous technological advancements play a crucial role in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of closed-loop recycling systems. Innovations in sorting, processing, and material characterization technologies can significantly enhance the quality and yield of recycled materials.
Research and development in new materials science and manufacturing processes are essential to maximize the use of recycled materials in diverse applications. This can unlock new opportunities for product innovation and further reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing.
Minimizing Hazardous Waste Generation and Proper Disposal
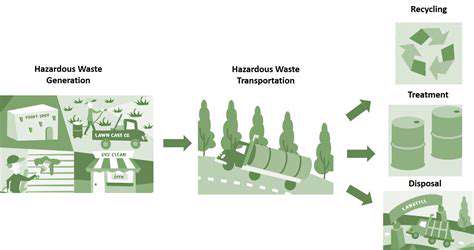
Minimizing Waste Generation Strategies
Implementing proactive strategies to minimize hazardous waste generation is crucial for environmental protection and cost savings. These strategies encompass a wide range of approaches, from process modifications and material substitutions to improved housekeeping and training. A key aspect of this approach is the identification of sources of hazardous waste within a facility or operation. By understanding where waste is generated, preventative measures can be targeted more effectively.
Waste reduction is a critical component of a comprehensive hazardous waste management plan. It's far more economical and environmentally sound to prevent waste from being created in the first place than to treat or dispose of it later. This approach not only saves resources but also mitigates the risks associated with hazardous materials.
Material Selection and Substitution
Choosing less hazardous materials is a crucial step in reducing hazardous waste. This often involves a thorough review of the materials used in various processes to identify alternatives with lower toxicity or reduced potential for generating hazardous byproducts. Careful consideration of the entire lifecycle of a material, from extraction to disposal, is essential when making these choices.
Implementing a robust material substitution program can significantly reduce the volume of hazardous waste generated. This approach requires collaboration between engineers, chemists, and environmental professionals to identify and evaluate suitable substitutes while maintaining the desired functionality and performance of the process.
Careful consideration should be given to the potential environmental impact of the chosen substitute, including its potential for generating other forms of pollution and its ultimate disposal methods.
Process Optimization and Housekeeping
Optimizing existing processes to reduce or eliminate the use of hazardous materials is a critical part of minimizing waste generation. Process modifications can include adjustments to reaction conditions, changes in equipment design, or the implementation of cleaner production techniques. These strategies can significantly reduce the amount of hazardous waste generated without sacrificing productivity.
Maintaining a clean and organized work environment is essential to preventing spills, leaks, and accidents that can lead to the generation of hazardous waste. Regular housekeeping practices, including proper storage and handling procedures, are critical for minimizing the risk of incidents and associated waste generation. A well-maintained work environment also contributes to a safer and more efficient workplace.
Regular training and awareness programs for personnel involved in handling hazardous materials are vital for preventing errors and ensuring safe practices. Educating employees about the risks associated with hazardous materials and the proper procedures for handling them significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents and the subsequent generation of waste.
Employee Engagement and Training for Waste Reduction Awareness
Importance of Employee Engagement
Employee engagement plays a crucial role in fostering a culture of waste reduction awareness. When employees feel valued, heard, and invested in the company's goals, they are more likely to actively participate in initiatives aimed at minimizing waste. This engagement translates into a collective effort, where everyone feels personally responsible for making a difference, leading to a significant reduction in overall waste generation. Companies that prioritize employee engagement often see improved productivity and morale as well as a demonstrably positive impact on waste reduction targets.
Creating opportunities for employees to share their ideas and concerns regarding waste management practices is vital. Open communication channels allow for the identification of potential problem areas and the development of innovative solutions. Encouraging feedback and active participation helps cultivate a sense of ownership and shared responsibility, which is essential for long-term sustainability in waste reduction efforts.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Effective waste reduction strategies require comprehensive training programs that equip employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement them. These programs should cover various aspects of waste management, including proper waste segregation, recycling procedures, and the use of sustainable alternatives. Training should be interactive and engaging, incorporating practical exercises and real-world examples to illustrate the impact of individual actions on overall waste reduction goals.
Regular refresher courses and workshops can reinforce learned concepts and address emerging challenges. It is crucial to tailor training to specific job roles and responsibilities, ensuring that employees understand the waste reduction procedures relevant to their daily tasks. This targeted approach maximizes the effectiveness of training by directly addressing the needs and concerns of each department.
Incentivizing Waste Reduction Behaviors
Incentivizing positive behaviors related to waste reduction can significantly boost employee participation and motivation. Recognition programs, rewards, and competitive challenges can create a sense of excitement and encourage employees to actively seek ways to reduce waste. This positive reinforcement fosters a culture of continuous improvement and encourages employees to go beyond basic compliance with waste management procedures.
Financial incentives, such as discounts or bonuses, can provide tangible motivation for employees to adopt sustainable practices. Non-monetary rewards, like public acknowledgment, employee of the month awards, and team recognition, can also be highly effective in fostering a culture of environmental stewardship. The key is to align incentives with company values and create a positive feedback loop that reinforces desired behaviors.
Measurement and Monitoring of Progress
Monitoring waste reduction efforts is essential to gauge the effectiveness of implemented strategies. Tracking waste generation rates, recycling percentages, and the overall impact of employee engagement initiatives allows for data-driven adjustments to existing programs. This data-driven approach enables companies to identify what works, what needs improvement, and what new initiatives might be necessary to meet their waste reduction targets.
Regular reporting and analysis of waste management data provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of training programs, engagement initiatives, and incentive programs. Analyzing the data allows for the identification of trends, patterns, and areas where further improvements can be made. This continuous monitoring and analysis are vital for achieving long-term success in waste reduction efforts.
Integration with Company Culture
Integrating waste reduction awareness into the company's overall culture is crucial for long-term sustainability. This integration ensures that waste reduction initiatives are not perceived as isolated programs but as an integral part of the company's values and operations. A strong company culture that values environmental sustainability fosters a sense of shared responsibility and promotes the adoption of sustainable practices across all levels of the organization.
Incorporating waste reduction principles into company policies, procedures, and daily operations demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility. Clear communication regarding company values and goals related to waste reduction helps employees understand their role in achieving those goals. By consistently reinforcing the importance of waste reduction through communication and action, companies can cultivate a genuinely sustainable culture.
Leadership Role Modeling
Leadership plays a pivotal role in setting the tone for waste reduction awareness. When leaders actively participate in and champion waste reduction initiatives, they demonstrate the importance of these efforts to the entire organization. This leadership commitment fosters a ripple effect, encouraging employees at all levels to embrace sustainable practices.
Leaders who embody waste reduction principles create a culture of accountability. Their actions serve as a powerful example, motivating employees to adopt similar behaviors. By leading by example, leaders can inspire a whole organization to embrace waste reduction as a shared responsibility, creating a more sustainable and environmentally conscious workplace.
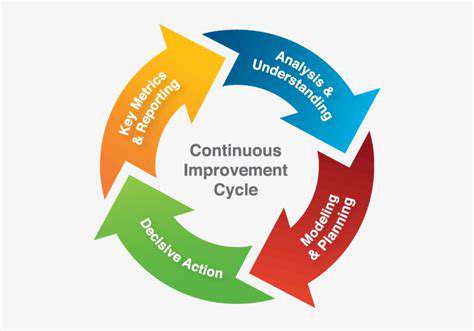
Measuring, Monitoring, and Reporting Performance Metrics for Continuous Improvement
Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
A crucial first step in measuring and monitoring performance is identifying the key performance indicators (KPIs) that truly reflect the success of your processes. These KPIs should be directly tied to your organizational goals and objectives. For example, if your goal is to improve customer satisfaction, KPIs might include customer satisfaction scores, the number of customer support tickets resolved, or the average response time to customer inquiries. Thorough consideration should be given to the specific metrics that will provide the most valuable insights for continuous improvement initiatives.
Selecting the right KPIs is not just about picking numbers; it's about choosing metrics that accurately represent the desired outcomes. A poorly chosen KPI can lead to misguided efforts and wasted resources. Carefully consider the data sources available and the frequency with which the data will be collected. The availability of reliable and consistent data is essential for accurate monitoring and reporting.
Implementing Monitoring Systems and Tools
Once your KPIs are defined, you need a robust system to collect and analyze the data. This might involve implementing specialized software, leveraging existing data platforms, or creating custom dashboards. The monitoring system should be designed to track KPIs in real-time or at regular intervals, providing timely insights into performance trends. This allows for proactive identification of potential issues and the ability to make adjustments before they escalate into significant problems. A well-designed monitoring system facilitates the collection of relevant data, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of performance evaluations.
Choosing the right monitoring tools is essential to ensure efficient data collection and analysis. Consider the ease of use, the data visualization capabilities, and the ability to integrate with existing systems. The tools should allow for easy access to data by relevant stakeholders, enabling quick identification of trends and potential issues. Flexibility in customizing reports and dashboards is critical to providing tailored insights for different teams and departments.
Furthermore, the monitoring system must be scalable to accommodate future growth and evolving needs. A rigid system will become increasingly cumbersome as the organization expands, potentially hindering the ability to effectively track and analyze performance metrics.
Developing Comprehensive Reporting Mechanisms
Regular reporting is vital for communicating performance insights and driving continuous improvement. These reports should be clear, concise, and easily understandable by all stakeholders, including executives, managers, and team members. Visualizations, such as charts and graphs, can effectively communicate trends and patterns in the data, making it easier to identify areas needing attention. Reports should highlight both successes and areas for improvement, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development.
The reporting process should be standardized and consistent to ensure that data is interpreted accurately across departments and teams. This consistency allows for meaningful comparisons and facilitates the identification of best practices. Regularly scheduled reports should be delivered to relevant stakeholders in a timely manner to enable prompt responses to emerging issues and opportunities.
The reports should also incorporate actionable recommendations based on the observed trends. This will empower teams to take corrective actions and implement improvements to optimize performance. A well-structured reporting process ensures that insights are not lost and that the organization can effectively use data to drive continuous improvement.