Embracing Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Innovative Material Choices for Eco-Friendly Packaging
The automotive aftermarket is constantly seeking ways to reduce its environmental footprint, and sustainable packaging is a crucial component of this effort. Manufacturers are exploring a wider range of innovative materials, moving beyond traditional plastics to embrace biodegradable and compostable options. This shift requires careful consideration of material properties, cost-effectiveness, and the entire lifecycle of the packaging, from production to disposal. For instance, utilizing plant-based materials like sugarcane or corn starch in packaging can significantly reduce reliance on petroleum-derived plastics, contributing to a greener supply chain.
Another key aspect is the development of more efficient and less wasteful packaging designs. Optimizing shape and size to minimize material use while ensuring product protection is a critical factor. This often involves collaborating with packaging suppliers and engineers to develop bespoke solutions tailored to specific aftermarket parts. The goal is to strike a balance between environmental responsibility and the practical needs of transporting and storing goods effectively.
Optimized Packaging Design for Reduced Waste
Waste reduction is a key driver in sustainable packaging solutions. Designing packaging that is easily recyclable or compostable is crucial. This involves selecting materials with readily available recycling infrastructure and ensuring clear labeling for proper disposal. Additionally, optimizing packaging size and shape to minimize material use while maintaining product safety is essential. Innovative design approaches like using folding cartons instead of rigid containers can lead to substantial reductions in material consumption and waste generation.
Streamlining the packaging process to eliminate unnecessary steps and materials is equally important. Minimizing the use of adhesives, tapes, and fillers can drastically reduce waste. Implementing automated packaging lines and using lightweight yet robust materials can further enhance efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of the packaging process.
The Role of Supply Chain Collaboration in Sustainable Packaging
Sustainable packaging isn't just about the materials themselves; it's also about the entire supply chain. Collaboration between manufacturers, logistics providers, and packaging suppliers is essential for implementing and scaling sustainable packaging solutions. Manufacturers must communicate their sustainability goals to their suppliers, encouraging them to adopt similar practices. Open communication and shared responsibility for environmental impact are key to successful implementation.
Effective communication and collaboration throughout the supply chain are vital for the successful adoption of sustainable packaging. Sharing best practices, data on material usage, and feedback on packaging performance can lead to continuous improvement. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and allows for the development of more sustainable and efficient packaging solutions for the automotive aftermarket. Partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability is essential for achieving long-term goals.
Transportation Efficiency and Packaging Durability
The transportation of aftermarket parts plays a significant role in the overall environmental impact. Sustainable packaging must not only be environmentally friendly but also durable enough to withstand the rigors of transportation. Lightweight materials that offer excellent protection against damage during transit can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Using optimized packaging configurations to maximize space utilization during transport can further enhance efficiency and reduce the environmental footprint of the logistics process.
Choosing the appropriate packaging materials and designs based on the specific transportation methods used is crucial for maintaining product integrity and minimizing waste. For example, using cushioning materials that absorb shock effectively, or incorporating reinforced structures to withstand vibrations during transit, are key considerations. Efficient packaging directly contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system for the automotive aftermarket.
Promoting Circular Economy Principles for Parts Recycling and Reuse
Understanding the Circular Economy
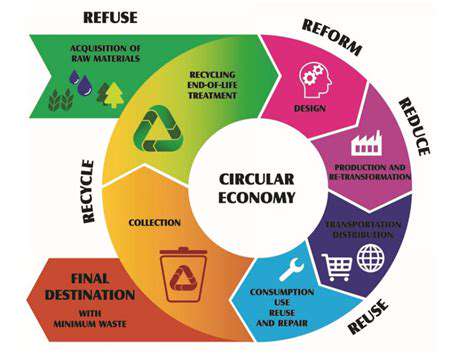
The circular economy represents a fundamental shift from the traditional linear take-make-dispose model of production and consumption. Instead of extracting resources, producing goods, and discarding waste, a circular economy aims to design out waste and pollution, keep products and materials in use, and regenerate natural systems. This approach is crucial for sustainability and resource efficiency, as our planet's finite resources are under increasing pressure.
Implementing circular economy principles is crucial for mitigating the environmental impacts of our current consumption patterns. By embracing reuse, repair, and recycling, we can significantly reduce our reliance on virgin resources and minimize waste generation. This transition is essential for building a more resilient and sustainable future.
Designing for Durability and Reusability
Companies can design products with durability and repairability in mind, extending their lifespan and reducing the need for frequent replacements. This approach fosters a culture of product longevity and minimizes the environmental impact associated with manufacturing new products.
By incorporating design principles that promote durability and reusability, we can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills and conserve valuable resources. This proactive approach is essential for achieving a truly circular economy.
Promoting Repair and Reuse
Encouraging repair and reuse initiatives is a cornerstone of the circular economy. Repair cafes, for example, provide opportunities for individuals to learn how to repair broken items, extending their useful life and reducing waste. This promotes a culture of resourcefulness and reduces the demand for new products.
Implementing Recycling and Waste Management Systems
Efficient recycling and waste management systems are vital for a circular economy. These systems should be designed to maximize material recovery and minimize contamination, ensuring that valuable materials are diverted from landfills and used in new products. This crucial component of the circular economy helps to conserve resources and reduce pollution.
This is essential for a truly circular economy, as it focuses on recovering valuable materials. Effective waste management practices are essential for closing the loop and minimizing environmental impact.
Investing in Research and Development
Investing in research and development is essential for innovation in the circular economy. This includes exploring new technologies for material recovery, developing innovative business models, and advancing sustainable design principles. Investment in research fosters the creation of new solutions and breakthroughs that drive the circular economy forward.
By funding research and development, governments and businesses can unlock new possibilities and drive positive change. This commitment to innovation is critical for achieving a sustainable and resilient future.
Collaboration and Policy Support
Collaboration between businesses, governments, and individuals is critical for effectively implementing circular economy principles. Governments can establish supportive policies, such as extended producer responsibility schemes, that encourage businesses to design for recyclability and take responsibility for product end-of-life management. Encouraging collaboration fosters a shared responsibility for creating a circular economy.
Consumer Education and Awareness
Educating consumers about the benefits of circular economy principles is crucial. Raising awareness of the importance of reducing consumption, reusing products, and recycling materials empowers individuals to make more sustainable choices. This change in consumer behavior is essential for driving a systemic shift towards a circular economy.
Educating consumers about the importance of responsible consumption is key to the success of a circular economy. Empowering individuals with knowledge and practical tools will help them to make sustainable choices and promote a more circular economy.
Technological Advancements in Green Logistics for the Automotive Aftermarket

Green Energy Solutions
Technological advancements in green energy have dramatically improved the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy sources. Solar panel technology, for instance, has seen significant progress in terms of cost reduction and power output, making solar energy a more viable option for homeowners and businesses. This progress is crucial in the fight against climate change, as it reduces reliance on fossil fuels and their associated environmental impact. The development of more efficient energy storage systems, like advanced batteries, is also a key component in the transition to a sustainable energy future. This allows for better management and utilization of intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind, further enhancing the overall sustainability of our energy grids.
Furthermore, innovative technologies are constantly emerging to improve the integration of renewable energy into existing power grids. Smart grids, equipped with advanced sensors and communication systems, enable better management of fluctuating energy production from renewable sources, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. These advancements are essential for the widespread adoption of renewable energy, as they address the challenges associated with its inherent variability. This transition is also facilitating the development of new industries and job opportunities in the green energy sector, contributing to economic growth and social progress.
Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing
The focus on sustainability extends beyond energy production to encompass the entire lifecycle of products. innovative materials science is driving the development of eco-friendly alternatives to traditional materials, such as plastics and metals. Bio-based plastics, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or algae, are becoming increasingly popular and offer a viable alternative to petroleum-based plastics, significantly reducing our dependence on finite resources. These materials contribute to a more circular economy, promoting resource efficiency and minimizing waste.
Sustainable manufacturing processes are also gaining prominence, with companies adopting strategies to reduce their environmental footprint. This includes minimizing water consumption, reducing waste generation, and utilizing less energy-intensive production methods. Such practices not only contribute to environmental protection but also enhance the efficiency and profitability of manufacturing operations.
The development of more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes is crucial for creating a future that is both environmentally friendly and economically viable. These advancements are essential for decoupling economic growth from environmental degradation and fostering a more sustainable and resilient global economy.
The use of recycled materials in manufacturing is another key aspect of this movement. Companies are increasingly incorporating recycled content into their products, reducing the demand for virgin materials and minimizing the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. This approach fosters a circular economy, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.