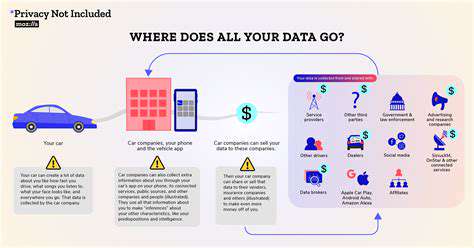
The Potential for Privacy Breaches
Understanding the Scope of Privacy Breaches
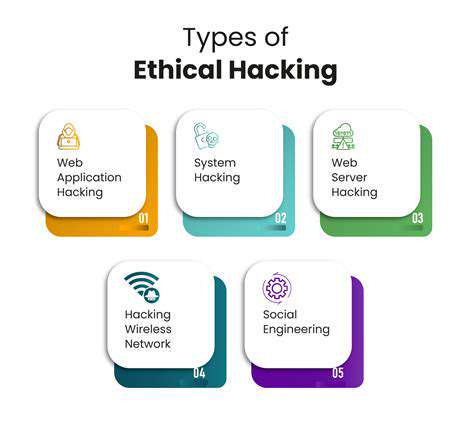
Data breaches are unfortunately a pervasive issue in today's interconnected world, affecting individuals and organizations alike. These breaches can expose sensitive personal information, including financial details, medical records, and even personal communications. The potential consequences of such exposures can range from financial losses to reputational damage, and even legal repercussions.
Understanding the various types of data breaches, from simple phishing scams to sophisticated hacking attacks, is crucial for mitigating the risk. Each type of breach necessitates a tailored approach to prevention and response.
The Impact on Individuals
Privacy breaches can have a profound impact on individuals. Stolen or compromised financial information can lead to significant financial losses, requiring extensive effort to restore accounts and rebuild trust. Furthermore, the disclosure of personal data can result in identity theft, which can have long-lasting repercussions on credit scores and overall well-being.
The emotional toll can be equally devastating, causing anxiety and distrust in the institutions that were supposed to protect their data.
The Impact on Businesses
Businesses face considerable risks from privacy breaches. Reputational damage can severely impact customer trust and loyalty, leading to a decline in sales and market share. Financial losses resulting from legal actions, regulatory penalties, and customer churn can also be substantial and long-lasting.
A breach can also result in significant operational disruptions, impacting productivity and causing delays in critical business processes.
Cybersecurity Measures
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential for preventing and mitigating the risk of privacy breaches. This includes strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, regular software updates, and employee training on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts. These preventative measures are crucial and can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful attack.
Data Encryption and Protection
Protecting sensitive data through robust encryption protocols and secure data storage practices is paramount. Data encryption transforms readable data into an unreadable format, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to access. Implementing encryption across all platforms and systems is a critical step in safeguarding sensitive information.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Ramifications
Adhering to relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is essential for preventing breaches. Non-compliance can result in substantial penalties and legal repercussions. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to substantial financial penalties and reputational damage.
Incident Response Planning
Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for effectively managing and mitigating the impact of a privacy breach. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, and responding to a breach. A well-defined incident response plan is essential for minimizing the damage and ensuring a swift and organized recovery.
User Empowerment and Control
User Empowerment in the Connected Car
User empowerment in the context of connected car services is crucial for establishing trust and ensuring responsible data usage. Drivers should have clear and comprehensive control over the collection, storage, and use of their personal data generated by their vehicles. This includes knowing exactly what data is being gathered, understanding how it's being used, and possessing the ability to modify or delete this information. Empowerment extends beyond simple consent mechanisms to active participation in defining the scope of data collection and application.
Control Over Data Collection
Users must have the ability to specify which data points their car collects. This granular control is essential to prevent the inadvertent or excessive gathering of personal information. For instance, users should be able to opt-out of location tracking in certain areas, limit the frequency of data transmission, and choose to not share specific data points like driving habits or preferred routes.
Transparency in data collection practices is paramount. Clear explanations of what data is collected, how it's used, and with whom it's shared must be readily available and easily understood. This transparency fosters trust and allows users to make informed decisions about their privacy.
Data Usage Transparency and Accountability
Connected car services should provide clear and concise explanations regarding the usage of collected data. Users must understand how their information is utilized, whether it's for improving vehicle performance, enhancing safety features, or providing personalized services. Accountability mechanisms are vital to ensure that data is used ethically and responsibly.
Data Security and Protection
Robust data security measures are essential to safeguard user data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. This includes encryption of data transmission, secure storage protocols, and regular security audits. Transparency in security measures and incident response plans is equally important to maintain user trust.
User Rights and Options
Users should have the right to access, correct, and delete their personal data. Clear procedures for exercising these rights must be readily available and easy to navigate. This includes the ability to request and obtain copies of collected data, amend inaccuracies, and request the deletion of data that is no longer needed.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Connected car services should collect only the minimum amount of data necessary to fulfill their intended purpose. Data collected should be directly relevant to the service being provided. This principle of data minimization ensures that personal information is not excessively collected or stored. Furthermore, the use of collected data should be limited to the stated purpose, preventing data from being used for unrelated or unintended purposes.
User Feedback and Grievance Mechanisms
Establishing clear channels for user feedback and addressing grievances is critical. Users should be able to report concerns, raise questions, and provide suggestions regarding data privacy and usage. Efficient and responsive grievance mechanisms build trust and encourage user participation in shaping the future of connected car services.
The Future of Data Privacy in the Automotive Industry

The Evolving Landscape of Data Regulations
Data privacy regulations are constantly evolving, adapting to the ever-changing technological landscape. This evolution is driven by public concerns about data security and misuse, as well as the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Governments worldwide are enacting stricter regulations to protect individuals' personal information, and these regulations are becoming more comprehensive and globally consistent. This dynamic environment requires businesses to adapt their data handling practices and adopt robust security measures to stay compliant.
The Rise of AI and Machine Learning
The proliferation of AI and machine learning technologies is transforming how data is collected, analyzed, and used. This raises new challenges for data privacy, as these technologies often require significant amounts of data to function effectively. Careful consideration must be given to the ethical implications of using AI and machine learning in ways that could potentially violate individual privacy rights. Transparent data usage policies and robust data governance frameworks are essential to ensure that AI development and deployment respects individual privacy.
The Importance of Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Data minimization, a core principle of many data privacy regulations, emphasizes collecting only the data absolutely necessary for specific, legitimate purposes. This principle is crucial for reducing the risk of data breaches and misuse, as well as for minimizing the potential for harm from unintended consequences. Purpose limitation further restricts the use of collected data, ensuring it is used solely for the stated purpose and not for unrelated activities. By adhering to these principles, organizations can better safeguard individual privacy and build trust with their users.
The Role of Data Security and Breach Response
Robust data security measures are essential for protecting personal information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are vital steps in this process. A well-defined breach response plan is critical to mitigate the impact of a data breach and ensure prompt notification to affected individuals. This plan should include procedures for containing the breach, conducting a thorough investigation, and implementing corrective actions to prevent future incidents.
The Impact of Global Interconnectedness
The increasing interconnectedness of the global economy and digital infrastructure necessitates a global approach to data privacy. International cooperation and harmonization of data privacy regulations are becoming increasingly important to address the complexities of cross-border data flows and transfers. Establishing international standards and frameworks for data protection will be crucial in ensuring consistent and effective protection of individual privacy rights in a globalized world. This will involve ongoing collaboration between governments, businesses, and international organizations.