Manufacturing Processes: Efficiency and Reduced Emissions
Optimizing Production Lines
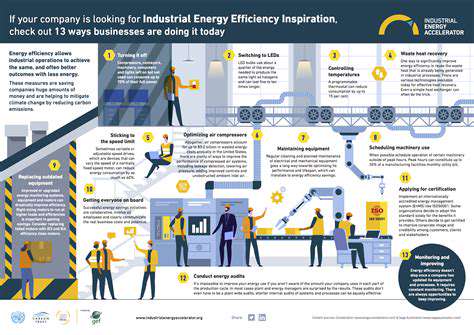
Streamlining manufacturing processes is crucial for achieving efficiency and profitability. By implementing lean manufacturing principles, companies can identify and eliminate waste, leading to significant improvements in productivity. This involves analyzing every step of the production line, from raw material procurement to final product delivery, to pinpoint areas where time and resources are being unnecessarily consumed. For example, reducing bottlenecks in assembly lines or optimizing material handling systems can dramatically increase output while minimizing operational costs.
Incorporating automation technologies can further enhance efficiency. Robotic process automation (RPA) can handle repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more strategic roles. Automated quality control systems, meanwhile, can ensure consistent product quality and reduce the likelihood of defects, leading to a significant return on investment. Integrating these technologies into existing workflows requires careful planning and execution, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
Material Handling and Logistics
Efficient material handling and logistics are essential components of a successful manufacturing process. Effective strategies for managing materials throughout the production cycle minimize downtime and improve overall output. This involves optimizing storage space, implementing inventory control systems, and ensuring timely and accurate delivery of raw materials. A well-designed system can significantly reduce logistical bottlenecks and ensure a smooth flow of materials throughout the production process, leading to improved production schedules.
Careful planning for material handling is crucial, considering factors such as material type, weight, and fragility. Using appropriate transportation methods and equipment ensures the safe and timely delivery of materials to the production line. This reduces delays and ensures the production process remains uninterrupted, which significantly impacts the company's bottom line.
Quality Control and Inspection
Maintaining high standards of product quality is paramount in the manufacturing sector. Implementing robust quality control measures throughout the production process minimizes defects and ensures customer satisfaction. This involves establishing clear quality standards, implementing rigorous testing procedures, and utilizing advanced inspection technologies. Early detection of defects can prevent costly rework and improve the overall efficiency of the production process.
Thorough inspection procedures at various stages of production, from raw materials to finished goods, are vital. Employing quality control systems that integrate automation and data analysis can further enhance the accuracy and speed of the inspection process. This proactive approach not only ensures high-quality products but also minimizes potential issues during later stages of production, leading to greater cost savings in the long run.
The environmental impact of auto parts production extends far beyond factory emissions. Consider that producing a single car tire consumes nearly 22 gallons of water. Innovators like Michelin now use recycled rubber and bio-sourced materials, cutting water usage by 30% while maintaining performance. These breakthroughs demonstrate that environmental responsibility and product quality aren't mutually exclusive.
Lifecycle Assessment and Continuous Improvement: Driving Sustainable Innovation
Lifecycle Assessment Fundamentals
A lifecycle assessment (LCA) is a systematic approach to evaluating the environmental impacts of a product or service throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. This comprehensive analysis considers all stages, including manufacturing, use, and end-of-life treatment, providing a holistic view of the environmental footprint. Understanding the environmental burdens at each stage is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and driving sustainable design choices. LCA helps to identify potential hotspots in the life cycle where environmental impacts are highest, enabling targeted interventions and resource optimization.
LCA methodologies vary, but generally involve data collection, impact assessment, and interpretation. This involves gathering data on energy consumption, water usage, emissions released, and material use at each stage. Impact assessment models translate these data points into potential environmental consequences, such as greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and resource depletion. Thorough data collection and robust methodologies are critical for reliable and meaningful LCA results.
Continuous Improvement in LCA
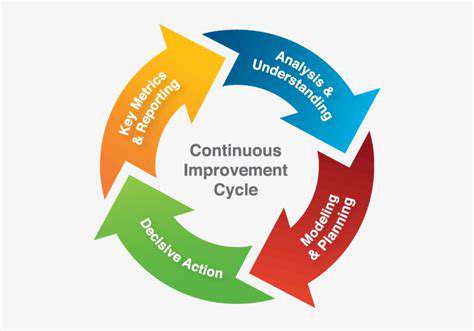
Continuous improvement in lifecycle assessment practices involves adopting innovative methodologies and technologies to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensiveness of the analysis. This includes the integration of advanced data analytics and modeling tools to streamline the process and identify previously overlooked environmental impacts. By leveraging technological advancements, companies can refine their LCA processes and derive more precise insights into their environmental performance. This in turn fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement, moving towards sustainable practices.
Adopting a continuous improvement approach to LCA means regularly reviewing and updating methodologies, ensuring they remain relevant and effective in addressing emerging environmental concerns. This iterative approach acknowledges the dynamic nature of environmental science and the evolving needs of stakeholders. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can ensure their LCA is a living document, reflecting the latest research and best practices in the field.
LCA and Sustainability Strategies
Lifecycle assessment plays a critical role in developing effective sustainability strategies by providing a framework for identifying and quantifying environmental impacts. By analyzing the environmental performance of products and services throughout their lifecycle, organizations can identify areas where improvements can be made and set targets for reducing their environmental footprint. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making and helps companies prioritize their sustainability initiatives. Companies can use the insights gained from LCA to develop targeted strategies to reduce their environmental impact.
Implementing LCA findings in sustainability strategies often involves developing eco-design principles, optimizing resource use, and implementing waste reduction programs. By integrating LCA into their decision-making process, companies can ensure that their products and services are designed and manufactured in an environmentally responsible manner. These proactive steps contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing the environmental impact of products and services.
LCA and Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement is a vital aspect of lifecycle assessment, as it ensures that the analysis addresses the concerns and priorities of various stakeholders. This includes engaging with customers, suppliers, communities, and regulatory bodies to understand their expectations and incorporate their feedback into the LCA process. By actively engaging with these stakeholders, companies can gain insights into the specific environmental concerns of different groups, which can influence the design and development of more sustainable products and services. This collaborative approach ensures the LCA is relevant and valuable to all parties involved.
Effective stakeholder engagement can lead to more comprehensive LCA studies by incorporating diverse perspectives and experiences. By understanding the needs and priorities of various stakeholder groups, companies can refine their LCA analysis to address the most critical environmental concerns. This inclusivity ensures that the LCA process is not limited to the company's internal perspective but also reflects the broader societal context.