Performance Standards and Testing Procedures
Performance Standards for Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, while promising a future of safer and more efficient transportation, require rigorous performance standards to ensure safety and reliability. These standards must address various aspects of the vehicle's operation, including its ability to perceive and react to its environment, its decision-making processes in complex situations, and its resilience to unexpected events. This involves defining specific metrics for object detection, path planning, emergency braking, and handling various weather conditions. Robust testing protocols are crucial to validating that these performance standards are met, and that the autonomous systems can handle the demands of real-world scenarios.
Furthermore, the performance standards must encompass a broad spectrum of scenarios, from simple highway driving to complex urban environments. This includes consideration for diverse traffic conditions, pedestrian interactions, and unexpected obstacles. These standards must be consistently applied across different manufacturers and models, ensuring a degree of uniformity and comparability in the performance of autonomous vehicles. This approach is vital for establishing public trust and confidence in the technology.
Testing Procedures for Autonomous Vehicles
Rigorous testing procedures are essential to validate the performance standards and ensure that autonomous vehicles operate safely and reliably. These procedures should involve a multi-faceted approach, encompassing simulations, controlled environments, and real-world testing. Simulations allow for controlled exploration of various scenarios and conditions, providing valuable data on system performance under different circumstances. This iterative approach helps to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before the vehicles are deployed on public roads.
Controlled environments, such as closed tracks and designated test areas, offer opportunities for focused evaluations of specific functionalities, such as lane keeping, obstacle avoidance, and emergency response. These testing grounds allow for the collection of detailed data on vehicle behavior and system performance, enabling engineers to make necessary adjustments and improvements. Real-world testing, in contrast, provides a more comprehensive evaluation in varied and unpredictable environments.
Data analysis from these testing procedures is critical to identifying potential issues and further refining the systems. The results will help to inform the development of more effective algorithms and hardware. The collection and analysis of data from real-world testing scenarios are particularly important for validating the performance standards in dynamic and unpredictable conditions. These testing procedures, encompassing simulations, controlled environments, and real-world scenarios, are crucial for building a robust and reliable autonomous vehicle system.
Legal Framework for Autonomous Vehicle Testing
The legal framework surrounding autonomous vehicle testing is critical to ensuring safety and accountability. This framework must address liability issues, data privacy concerns, and the ethical implications of autonomous decision-making. It is essential to establish clear guidelines for testing environments, data collection practices, and reporting mechanisms. This framework should also consider the potential for human error in the design and implementation of autonomous vehicles. Furthermore, it is important to define the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders, such as manufacturers, regulators, and users.
The legal framework must also address the complexities of liability in case of accidents involving autonomous vehicles. Who is responsible—the manufacturer, the software developer, or the user—needs to be clearly defined. This aspect is paramount to fostering public trust and confidence in the technology. Clear legal guidelines are vital for establishing a robust framework for autonomous vehicle development and deployment, ensuring safety and accountability for all involved parties.
Furthermore, the framework must encompass privacy regulations related to the vast amounts of data collected by autonomous vehicles during testing and operation. The collection and use of this data must be governed by strict ethical and legal standards to protect user privacy. This is crucial to mitigating potential risks and ensuring responsible development and implementation of the technology. The legal framework must evolve to address the unique challenges posed by autonomous vehicles, promoting innovation while upholding safety standards.
Liability and Insurance Considerations
Understanding Liability in Autonomous Vehicle Accidents
Determining liability in accidents involving autonomous vehicles presents a unique challenge to the existing legal framework. Current laws and regulations often hinge on human error as a primary factor in determining fault. However, with autonomous vehicles, the concept of who is at fault becomes significantly more complex. Is it the manufacturer for a software defect? Is it the owner for improper use? Or is it the vehicle itself, in a sense, acting as an independent agent?
This uncertainty necessitates a careful examination of the existing legal landscape and the development of new legal precedents to effectively address the potential for accidents involving these revolutionary technologies. The legal community is working diligently to establish clear guidelines and responsibilities, but the evolving nature of autonomous vehicles requires a dynamic and adaptable approach to liability.
Insurance Coverage for Autonomous Vehicles
Insurance providers are grappling with the implications of autonomous vehicles on their current coverage models. Traditionally, insurance policies are predicated on human drivers and their actions. Autonomous vehicles, however, operate without human intervention, requiring a re-evaluation of existing policies. New policies will likely need to address factors such as the vehicle's software, the manufacturer's liability, and the potential for malfunctions or unforeseen circumstances.
The insurance industry is exploring innovative approaches to cover potential risks. This includes establishing specific coverage for autonomous vehicle-related accidents, differentiating between incidents caused by software glitches and those due to external factors, and potentially implementing tiered insurance plans based on the level of autonomy.
Manufacturer Liability in Autonomous Vehicle Accidents
Determining manufacturer liability in accidents involving autonomous vehicles is a critical aspect of the legal framework. Questions arise regarding the responsibility for defects in the vehicle's software, hardware, or design. It is crucial to establish clear lines of responsibility to ensure accountability and encourage the development of safe and reliable autonomous vehicles. This includes potential liability for inadequate testing, failure to address reported software bugs, or neglecting to implement necessary safety protocols.
The legal implications of manufacturer liability are significant, potentially impacting the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. This necessitates a careful balance between encouraging innovation and protecting consumers from potential harm.
Third-Party Liability in Autonomous Vehicle Accidents
Accidents involving autonomous vehicles often implicate third parties, such as pedestrians, cyclists, or other drivers. Defining liability when an autonomous vehicle is involved in a collision with a human-operated vehicle or a non-vehicle entity requires careful consideration. Establishing clear guidelines for determining fault in these situations will be crucial in establishing a standardized legal approach for resolving such collisions and to help prevent future accidents.
The potential for disputes and disagreements related to third-party liability necessitates a framework that considers the unique circumstances of autonomous vehicle operation. This should include provisions for liability in cases where human error, system malfunctions, or unforeseen events contribute to the accident.
Cybersecurity and Liability in Autonomous Vehicles
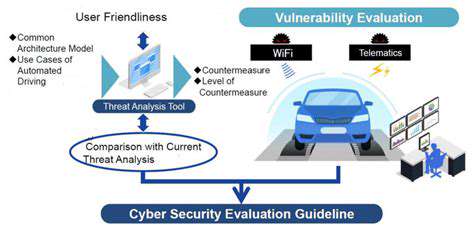
Autonomous vehicles are highly vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could lead to catastrophic accidents. The potential for malicious actors to manipulate the vehicle's systems poses a significant risk. Consequently, ensuring cybersecurity measures are robust and effective is paramount to the safe and reliable operation of autonomous vehicles. Legislation and regulatory oversight must address cybersecurity vulnerabilities, establishing standards for secure software development and maintenance.
Regulatory Framework for Autonomous Vehicle Insurance
Developing a comprehensive regulatory framework for autonomous vehicle insurance is essential to fostering public trust and ensuring responsible innovation. This framework should encompass guidelines for insurance coverage, liability procedures, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Clear regulations will provide a stable environment for the autonomous vehicle industry to operate and inspire public confidence in the technology.
This framework must adapt to the evolving technological landscape of autonomous vehicles to ensure that insurance policies and legal procedures effectively address the unique challenges presented by this emerging technology. A flexible and adaptable regulatory approach is necessary to accommodate advancements and potential unforeseen circumstances within the autonomous vehicle industry.