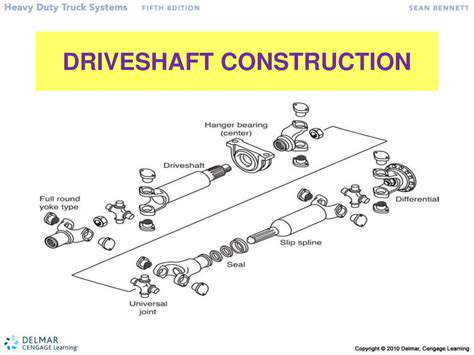
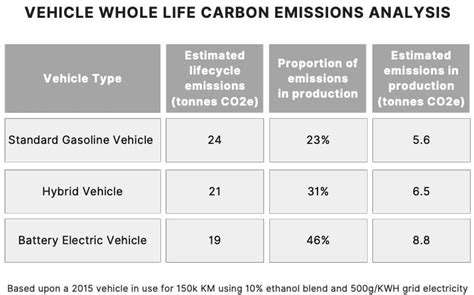
Workforce Expenses and Operational Costs
Labor Expenses in Battery Replacement
Battery replacement labor costs for electric vehicles show considerable variation based on multiple factors. These include replacement procedure complexity, specific vehicle model, and repair facility location. Urban shops typically face higher operational expenses, resulting in elevated labor rates compared to rural counterparts. Technicians with specialized EV repair expertise generally command premium wages, further affecting overall service costs.
Operational Expenses and Their Influence
Shop overhead includes multiple cost components: facility rental, utilities, insurance, and administrative staff compensation. These expenses typically factor into labor rates, meaning higher overhead leads to increased battery replacement pricing. Specialized equipment required for EV battery work, including diagnostic tools and battery handling apparatus, adds to operational costs. The necessity for technician training programs also contributes to the overall expense structure of EV battery replacement services.
Geographic Variations in Labor Costs
Regional differences significantly affect labor pricing. High-cost metropolitan areas typically feature elevated service rates across all sectors, including EV battery replacements. This stems from increased demand for skilled labor and the greater expenses associated with urban business operations. Local economic conditions and technician availability also influence regional labor costs.
Replacement Complexity and Service Duration
Battery replacement complexity serves as a primary determinant of labor expenses. Some EV models require more extensive disassembly and reassembly procedures than others. Battery removal and installation often demand specialized tools and careful handling to ensure safety and precision. The total service time, from initial assessment to final testing, directly correlates with overall labor costs. Technician experience and efficiency significantly affect this time component.
Vehicle Type Impact on Service Costs
Electric vehicle model differences substantially influence battery replacement expenses. Various models feature distinct battery configurations and access points. Some designs may require specialized equipment or extensive component removal, resulting in longer service times and higher costs. Battery pack dimensions and weight also affect replacement complexity and necessary equipment, creating significant cost variations between EV models.
Dealership vs. Independent Repair Options
The choice between manufacturer-affiliated and independent repair shops can substantially affect battery replacement costs. Dealerships often benefit from lower overhead, potentially offering reduced labor rates. However, independent shops may provide specialized EV battery expertise or unique equipment. Additional considerations include warranty coverage, customer service quality, and shop reputation. Parts availability and technician training requirements may also influence this decision.
Monitoring and understanding key performance indicators (KPIs) remains essential for evaluating success in any field. Effective KPI selection directly influences progress assessment and helps identify improvement opportunities. A well-designed KPI framework enables consistent performance tracking and provides comprehensive operational insights. This analytical approach ensures decision-making based on factual data rather than assumptions.
Battery Technology Evolution: Current Developments
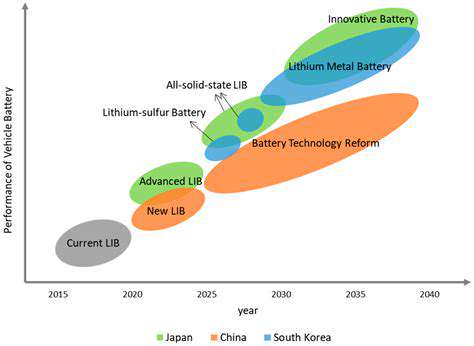
Dominance of Lithium-ion Technology
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have established market dominance in portable electronics and electric vehicles due to superior energy density, extended lifespan, and minimal self-discharge. Their widespread implementation has transformed multiple industries, providing a compelling replacement for traditional battery solutions. These batteries also offer significant advantages in weight and size reduction compared to alternatives.
LIB operation involves reversible lithium ion movement between electrodes during charging and discharging cycles. This characteristic enables efficient energy storage and retrieval.
Electrolyte Characteristics and Function
The electrolyte serves as a critical battery component, facilitating lithium ion transfer between electrodes. Its properties, including ionic conductivity and chemical stability, directly affect performance, safety, and operational lifespan. Electrolyte selection profoundly impacts voltage range and overall system efficiency.
Different electrolyte formulations offer varying safety and performance profiles. Understanding these differences remains crucial for optimal battery design and reliable operation.
Cathode Innovations and Energy Storage
Cathode materials store lithium ions during charging and release them during discharge. Material selection significantly influences energy density, operating voltage, and cycle durability. Continuous cathode material development focuses on improving these vital parameters.
Research emphasizes materials with increased capacity and enhanced thermal stability to boost performance and safety.
Anode Materials and Capacity Enhancement
Anode materials critically affect lithium-ion battery capacity and overall performance. Their lithium ion accommodation capability during charging/discharging directly determines total energy storage potential. Different materials demonstrate varying capacities and charge/discharge rates.
Common materials include graphite and silicon-based anodes, with ongoing research addressing their limitations and improving performance.
Temperature Regulation for Safety
Effective thermal management systems prove essential for safe lithium-ion battery operation. Excessive heat generation during charge/discharge cycles may trigger thermal runaway, creating significant safety hazards. Proper temperature control remains critical for preventing dangerous situations.
Advanced cooling methods and materials help dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating conditions.
Safety Considerations in Battery Design
Battery safety represents a paramount concern, particularly for electric vehicles and portable electronics. Identifying and mitigating potential risks like thermal runaway and electrical shorts proves essential for safe operation. Modern battery designs incorporate multiple safety features to minimize incident risks.
Continuous research focuses on improving safety through innovative materials and design approaches.
Future Prospects and Technological Breakthroughs
Battery technology's future depends on innovations across multiple domains. Researchers are investigating new chemical formulations, advanced materials, and novel designs to enhance energy density, safety, and cost efficiency. This includes solid-state battery development, which may overcome current lithium-ion technology limitations.
Significant research investment remains crucial for advancing battery technology and enabling broader application across industries.