Rethinking Urban Mobility
Modern urban environments grapple with complex challenges in managing traffic while ensuring smooth movement for residents. Outdated road designs frequently fail to meet the needs of growing vehicle numbers, expanding populations, and eco-friendly transport alternatives. This situation demands a thorough reassessment of current infrastructure with forward-looking strategies that balance motorist needs with pedestrian and cyclist safety through integrated systems.
Effective urban transport solutions form the backbone of economic progress, enhanced living standards, and minimized ecological footprints. Cities must explore cutting-edge methods including smart traffic controls, protected bicycle paths, and expanded transit options while maintaining accessibility for all community members.
Prioritizing Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety
Urban walkers and cyclists routinely navigate dangerous conditions due to insufficient infrastructure. Creating safer conditions for these vulnerable groups remains essential for building truly inclusive cities. Solutions include clearly marked crosswalks, better wayfinding signs, and properly maintained bicycle routes.
Protected bike lanes and dedicated crossings dramatically lower accident risks between motorists and non-motorized travelers. Well-planned infrastructure not only prevents injuries but also promotes active lifestyles while decreasing dependence on personal automobiles.
Enhancing Public Transportation Systems
Mass transit serves as a crucial tool for easing traffic jams and supporting sustainable city movement. Upgrading and extending public transport networks ensures convenient access for all urban dwellers through improved bus systems, subway expansions, and unified payment methods.
Expanded transit options can relieve choked roadways while cutting harmful emissions. These improvements lead to cleaner air, healthier communities, and more sustainable urban development. Increased ridership also stimulates local economies through new employment opportunities and supporting industries.
Integrating Technology for Smart Mobility
Incorporating digital solutions into city infrastructure optimizes traffic patterns through intelligent transport networks. Adaptive signal systems can modify timing based on real-time conditions, minimizing delays. Navigation tools using live data help drivers select optimal routes.
Smart mobility technologies substantially enhance both the efficiency and security of urban travel. Emerging innovations like connected and self-driving vehicles may transform urban transportation by addressing persistent traffic and safety challenges.
Promoting Sustainable Urban Design
Eco-conscious city planning principles create more livable and durable communities through green spaces, mixed-purpose developments, and environmentally friendly construction materials. These approaches emphasize ecological protection and resource efficiency.
Sustainability-focused design ensures urban growth benefits both the environment and local residents. This philosophy fosters healthier city ecosystems that improve quality of life while supporting long-term urban viability.
Optimizing Traffic Flow and Reducing Congestion
Improving Intersection Efficiency
Enhancing intersection operations remains vital for easing congestion and boosting safety. Careful signal programming and geometric design profoundly influence how well these critical junctions function. Effective planning must account for peak traffic volumes, pedestrian movements, and turning patterns to optimize vehicle throughput.
Smart traffic lights using real-time data can further improve intersection performance. These adaptive systems modify signal timing dynamically to match changing traffic conditions, reducing wait times while maximizing capacity during varying demand periods.
Enhancing Road Network Design
Strategic roadway planning forms the foundation for smooth traffic movement. Thoughtful road placement and connectivity significantly decrease congestion while shortening travel durations. Key considerations include proper lane configurations, thoroughfare dimensions, and multimodal integration to create cohesive transportation networks.
Highway access point planning requires particular attention, as properly spaced ramps with smooth transitions between road types maintain continuous traffic progression.
Promoting Alternative Transportation
Encouraging non-automotive transport options like mass transit, cycling, and walking can meaningfully reduce roadway crowding. Substantial investments in public transit, protected bike lanes, and pedestrian infrastructure can shift significant traffic volume from private cars. This modal transition decreases congestion while improving urban air quality.
Utilizing Technology for Traffic Management
Advanced traffic monitoring systems and intelligent transport technologies provide powerful tools for optimizing flow. Real-time data allows drivers to adjust routes dynamically, avoiding problem areas and improving overall network performance. Analytical insights from these systems help identify patterns, predict trouble spots, and develop targeted solutions.
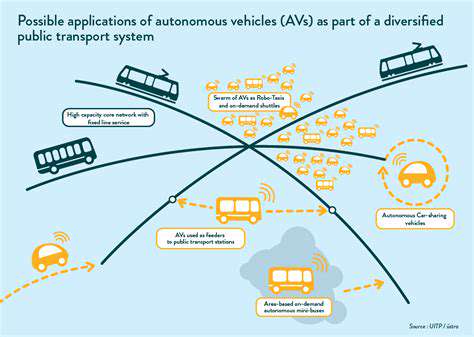
Connected and autonomous vehicles may eventually transform traffic management, though realizing their full potential requires substantial infrastructure upgrades and policy evolution.
Transforming Parking and Land Use
Autonomous Vehicles and Parking Revolution
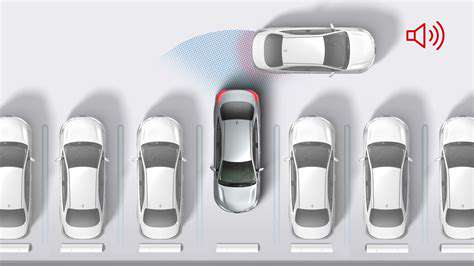
Self-driving vehicles will dramatically alter urban parking requirements. As cars gain autonomous parking capabilities, massive parking areas may become obsolete, potentially freeing land for housing, parks, and other community assets. These changes carry significant implications for city planners.
Future scenarios might include repurposed parking structures as mixed-use developments or converted lots as public gathering spaces. While these transformations offer exciting possibilities for urban vitality, they require phased implementation strategies balancing technological evolution with community needs.
Reimagining Urban Spaces
Autonomous technology's impact extends beyond parking infrastructure. Reduced reliance on traditional traffic management could enable more pedestrian-focused urban designs with enhanced public transit systems.
Cities might develop more concentrated, walkable districts featuring expanded green spaces and fewer vehicles, potentially improving environmental conditions and resident well-being.
Land Use Optimization
Diminished parking needs create substantial opportunities for land repurposing. Freed space could support various uses including residential projects, commercial developments, or ecological zones, collectively enhancing urban sustainability and livability.
Public Transportation Integration
Autonomous vehicles could complement mass transit networks, potentially decreasing private car dependence and creating more comprehensive mobility solutions benefiting both environmental and economic outcomes.
Economic Impacts and Job Creation
The autonomous transition will reshape multiple economic sectors, creating new industries while requiring adaptation in existing fields. This period offers both challenges and opportunities for employment in vehicle automation, supporting technologies, and infrastructure development.
Infrastructure Adaptation
Cities must evolve their physical frameworks to accommodate autonomous technologies, including charging networks, communication systems, and potentially redesigned thoroughfares. Successful integration demands significant investment and coordinated planning.
Ethical Considerations and Policy Changes
Autonomous vehicle adoption raises important ethical questions regarding accident responsibility and data security. Developing appropriate regulations and building public trust in these systems remain critical for successful implementation.
Vehicle preservation extends beyond basic sheltering; it's fundamental to maintaining automotive condition and value. Appropriate storage practices substantially mitigate environmental damage from temperature extremes, humidity, and UV exposure. These protective measures prolong exterior finishes, interior components, and mechanical systems, delivering long-term financial benefits.