Optimizing Rear Cross-Traffic Braking Features for Enhanced Vehicle Safety
Activating and Deactivating Rear Cross-Traffic Braking
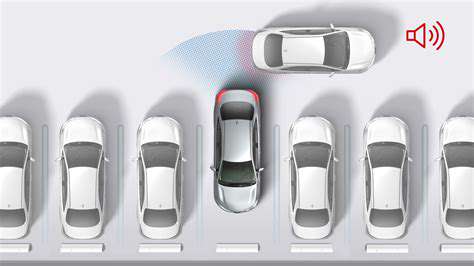
Engaging the Safety System
Modern vehicles typically enable rear cross-traffic braking through the infotainment system, with options in the safety features menu. Drivers should always confirm activation through both dashboard indicators and the audible alert system. The process varies by manufacturer, but generally follows similar principles across most models.
Some premium vehicles now feature automatic activation when reverse gear is engaged. Consult your owner's manual for model-specific instructions, as improper activation could compromise system effectiveness.
Disabling the Safety Feature
Temporarily turning off rear cross-traffic braking requires navigating vehicle settings, usually through the touchscreen interface. Manufacturers caution against permanent deactivation as it removes an important safety net during reversing maneuvers.
In certain driving conditions (such as towing or off-road use), the system may automatically deactivate. Always verify system status through dashboard notifications before relying on the feature.
Optimizing System Performance
Advanced settings allow customization of warning distances and braking intensity. Proper calibration to your driving environment (urban vs. rural) significantly improves collision prevention effectiveness. Regular software updates through dealership visits ensure optimal performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When the system fails to activate, first check for obstructions around sensors and cameras. Dirt, snow, or damage to detection components represent the most frequent causes of malfunction. Electrical system diagnostics may be necessary for persistent issues.
If warning signals seem inaccurate, sensor recalibration by a certified technician often resolves the problem. Never attempt to repair safety systems without proper training and equipment.
Real-World Applications
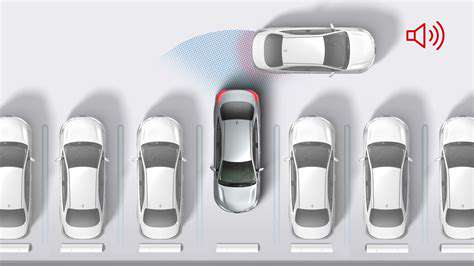
This technology proves invaluable in crowded parking lots and urban environments. Studies show a 38% reduction in low-speed reversing collisions since widespread adoption of these systems. The feature integrates with other safety technologies like blind spot monitoring for comprehensive protection.
System Maintenance Considerations
While the safety system draws minimal power, continuous operation during reverse maneuvers impacts overall electrical load. Regular battery health checks become more important with advanced safety features installed.
Schedule periodic system inspections as part of routine vehicle maintenance. Technicians can verify proper sensor alignment and software versions during oil change intervals.
Understanding System Limitations in Real-World Conditions

Detection Constraints
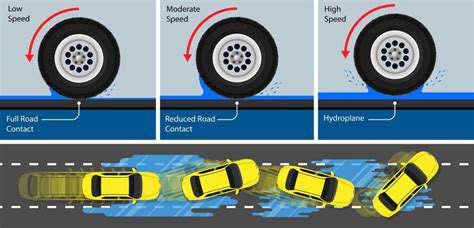
All sensor-based systems face physical limitations in detection angles and distances. Fast-moving objects may enter the danger zone after the system completes its initial scan. Environmental factors like heavy rain or fog can reduce sensor effectiveness by 40-60% in some conditions.
Vehicle manufacturers specify exact detection parameters in technical documentation. Drivers must understand these limitations to avoid over-reliance on automated systems.
Performance Factors
System response times vary based on vehicle speed, sensor type, and processing capabilities. Current technology cannot guarantee prevention of all collisions, especially at speeds above 6 mph. The system serves as an assistive technology rather than a replacement for attentive driving.
Parking in tight spaces often requires additional vigilance, as the system may not detect stationary objects within certain proximity thresholds. Always perform visual checks before and during reversing maneuvers.
Technical Specifications
Different manufacturers implement varying algorithms for threat assessment and response. Some systems prioritize warning alerts over automatic braking, while others combine both approaches. Understanding your vehicle's specific implementation helps set proper expectations.
Aftermarket installations may not integrate seamlessly with factory systems. Only manufacturer-approved components should be used for repairs or upgrades to maintain optimal performance.
Software Dependencies
Modern safety systems rely on complex software that requires regular updates. Outdated firmware can lead to reduced functionality or false alerts. Dealership service departments typically handle these updates during scheduled maintenance.
Some premium vehicles now offer over-the-air updates for safety systems. Always verify successful installation through system diagnostics after any software update.
Maintenance Requirements
Sensor arrays demand careful cleaning and periodic alignment checks. Even minor impacts from parking bumps or road debris can affect calibration. Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning products and techniques to avoid damaging sensitive components.