The Growing Threat Landscape for Connected Car Remote Access
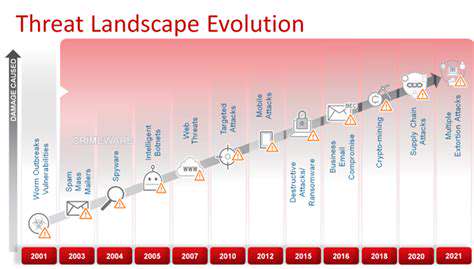
The Evolving Nature of Cyber Threats
The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new and sophisticated attacks emerging regularly. This dynamic environment requires organizations to adapt their security strategies and practices to stay ahead of the curve. Traditional security measures often prove insufficient against these advanced threats, demanding a proactive and layered approach to cybersecurity. The rise of ransomware, phishing, and other malicious activities necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape and its potential impact.
The Role of Malicious Actors
malicious actors, ranging from sophisticated state-sponsored groups to opportunistic individuals, pose a significant threat. These actors are often highly motivated and well-resourced, developing increasingly sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to sensitive data. Understanding the motivations and tactics of these actors is crucial in developing effective countermeasures. The constant innovation in their attack methods makes staying vigilant and adapting to new threats a critical aspect of cybersecurity.
The Importance of Vulnerability Management
Vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and configurations are often exploited by attackers. Proactive identification and remediation of vulnerabilities are essential for mitigating the risk of successful attacks. Regular security assessments, penetration testing, and patch management are crucial to maintain a strong security posture. This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of successful exploitation of vulnerabilities, and safeguards the integrity of systems and data.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The proliferation of emerging technologies, such as IoT devices and cloud computing, introduces new attack vectors and complexities to the threat landscape. These technologies often lack robust security features, making them attractive targets for attackers. Protecting these interconnected systems and ensuring data integrity in the cloud requires specialized security measures. Furthermore, the reliance on these technologies creates a more interconnected and potentially vulnerable environment.
The Need for Enhanced Security Awareness Training
Employee training plays a critical role in preventing successful attacks. Security awareness training programs that educate employees about common threats, like phishing scams and social engineering tactics, are essential. Equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and report suspicious activity significantly reduces the risk of successful attacks. Regular training sessions and ongoing reinforcement are crucial components of a robust security strategy.
The Significance of Incident Response Planning
Having a well-defined incident response plan is critical for effectively managing and mitigating the impact of a cyberattack. This plan should outline procedures for identifying, containing, and recovering from a security breach. A robust incident response plan minimizes the damage from a security breach, limits the exposure of sensitive data, and helps in maintaining business continuity. Testing and practicing these plans are crucial for their effectiveness in a real-world scenario.
Vulnerabilities in Remote Access Protocols and Systems
Security Risks of Unpatched Software
Outdated or unpatched remote access software is a major vulnerability. Exploitable security flaws in these applications can be readily found and exploited by malicious actors. These vulnerabilities can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, systems, and networks. Patches often address these issues, making it crucial to keep software updated to mitigate these risks.
Regularly updating remote access software is a fundamental security practice. By promptly installing security updates, you substantially reduce the risk of exploitation by attackers. This proactive approach is vital in protecting your systems from potential breaches and data loss.
Weak Passwords and Authentication
Weak or easily guessed passwords are a common cause of breaches in remote access systems. Using strong, unique passwords for each account is critical for robust security. Employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security by adding an extra layer of protection beyond a simple password. This adds an extra hurdle for malicious actors to overcome.
Password managers can help ensure the creation and use of complex, unique passwords across multiple accounts. This can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful breach.
Insufficient Network Security
Poor network security configurations can expose remote access points to attacks. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are crucial components for safeguarding your network. Properly configured firewalls can block unauthorized access attempts and limit the impact of potential breaches. Implementing robust access controls is essential for managing who can connect to your systems.
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for remote connections creates an encrypted connection, masking the traffic from external entities. This greatly enhances the security of your network and its resources.
Lack of Employee Training
Phishing attacks and social engineering tactics frequently exploit vulnerabilities in human behavior. Employees who lack the proper training and awareness of these threats are more susceptible to falling victim to these attacks. Providing thorough security awareness training is paramount for a strong security posture. This training should cover topics such as identifying phishing emails, recognizing social engineering attempts, and reporting suspicious activities.
Inadequate Access Controls
Insufficient access controls allow unauthorized users to access sensitive data and systems. Implementing strong access controls limits access to only authorized personnel, and prevents unnecessary exposure of data. Granular access permissions ensure that users only have access to the resources they require for their job functions.
Using least privilege access principles, which limits user privileges to only those necessary to perform their tasks, significantly reduces the impact of a potential breach. This minimizes the potential damage in the event of a successful attack.
Vulnerable Remote Desktop Protocols
Remote Desktop Protocols (RDP) are frequently used for remote access. These protocols, however, can be vulnerable to attacks if not properly secured. Regularly patching and updating RDP servers is essential for maintaining security. Employing strong authentication methods and limiting access to authorized users is equally important. Configuring the RDP server with secure settings can prevent unauthorized access.
Physical Security Risks
Physical security vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access to remote access devices. Protecting physical access to servers and network equipment is critical, especially in shared environments. Implementing physical security measures, such as access control systems, and monitoring, is crucial to reduce the risk of physical compromise. Protecting the physical location of remote access equipment is an often overlooked but significant aspect of overall security.
Mitigating Risks Through Robust Security Measures
Protecting Against Malware
A critical aspect of cybersecurity for connected cars is the implementation of robust anti-malware measures. Malicious software can compromise the vehicle's systems, potentially allowing attackers to gain control of critical functions like braking, steering, and acceleration. This could lead to catastrophic consequences, making robust anti-malware solutions paramount. Continuous monitoring and proactive threat detection are essential to identify and neutralize malware before it can cause significant damage.
Securing Communication Channels
The increasing reliance on wireless communication in connected vehicles necessitates enhanced security protocols for data transmission. Protecting the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged between the vehicle and external systems is crucial. This includes employing encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive information, such as driver location data or vehicle diagnostics. Strong authentication mechanisms are also essential to verify the identity of communicating parties and prevent unauthorized access.
Vulnerability Management
Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are vital for identifying and addressing potential security weaknesses in the vehicle's software and hardware. This proactive approach helps to mitigate risks before attackers exploit vulnerabilities. Patches and updates should be implemented promptly to close security gaps and maintain the integrity of the system. A robust vulnerability management process is critical to ensure the ongoing security of connected cars.
Data Encryption and Privacy
Protecting the privacy of driver data is paramount in the context of connected cars. Sensitive information, such as location data and driving habits, must be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access and misuse. Data anonymization techniques can further enhance privacy by removing identifying information while still allowing for valuable data analysis. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations is essential to build trust and confidence in connected vehicle technologies.
Physical Security Measures
Physical security is often overlooked but equally important in the context of connected car cybersecurity. Protecting the vehicle's hardware components, such as the embedded systems and communication modules, from physical tampering or unauthorized access is crucial. This includes implementing secure storage areas for sensitive components and employing physical barriers to prevent unauthorized access. Robust physical security measures are a necessary complement to software-based security protocols.
User Authentication and Access Control
Effective user authentication and access control mechanisms are necessary to limit access to vehicle systems based on user roles and permissions. This helps to prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to sensitive information or controlling critical vehicle functions. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control can significantly enhance the security posture of the connected car. Careful consideration of user access privileges is critical to maintaining system integrity.
Incident Response and Recovery
Establishing a comprehensive incident response plan is essential to effectively manage security breaches and ensure a swift and organized recovery process. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, and resolving security incidents. Regularly testing and updating the incident response plan is critical to ensure its effectiveness in real-world scenarios. A dedicated team with the expertise to handle security incidents is vital for minimizing downtime and mitigating potential damage.
The Role of Industry Standards and Regulations

Defining Industry Standards
Industry standards are crucial for ensuring compatibility, interoperability, and consistency within a specific sector. They establish a common language and set of guidelines that allow different companies and organizations to work together seamlessly. These standards are essential for the smooth functioning of complex systems and processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. Furthermore, they foster innovation by providing a framework for new technologies and approaches to be developed and implemented.
Without standardized procedures and specifications, the development and integration of products and services would become significantly more challenging and costly. This would hinder progress and potentially create significant market inefficiencies.
Benefits of Adhering to Standards
Adherence to industry standards brings a host of benefits, ranging from improved interoperability to increased efficiency. Products and services built on standardized platforms can integrate seamlessly, leading to quicker deployment and easier maintenance. This streamlined approach significantly reduces the time and resources required for development and implementation, ultimately benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Furthermore, consistent standards help foster competition by ensuring that products and services are comparable. This level playing field promotes innovation and allows consumers to make informed choices based on clear and consistent specifications.
The Impact of Standards on Innovation
While some might perceive standards as restrictive, they actually play a vital role in fostering innovation. Standards provide a foundation upon which new technologies and approaches can be built. Innovation often thrives when existing frameworks are leveraged, allowing developers to focus on new features and functionalities rather than reinventing the wheel. By establishing a shared platform, standards encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing, leading to breakthroughs that would otherwise be unattainable.
Maintaining Standards and Keeping Pace with Technology
Maintaining industry standards requires ongoing efforts to adapt to evolving technologies and changing market demands. This involves continuous evaluation and updates to existing standards to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Organizations must proactively engage in this process to stay competitive and ensure their products and services remain relevant and functional.
The Role of Standardization Bodies
Standardization bodies play a crucial role in defining, developing, and maintaining industry standards. These organizations bring together experts from various sectors to create comprehensive and well-defined guidelines. Their efforts ensure that standards are aligned with current technologies and address emerging needs.
This collaborative process is essential for creating standards that are both effective and adaptable. It allows the standards to be revised and updated as needed to reflect changing technological advancements and industry best practices. This dynamic approach ensures that standards remain relevant and impactful over time.
Challenges in Implementing Standards
Implementing industry standards can present several challenges, including the need for significant investments in training and infrastructure. Organizations must invest time and resources to ensure their operations are aligned with the new standards, which can be a substantial undertaking. Moreover, there can be resistance to change from stakeholders who are accustomed to existing procedures.
The Future of Industry Standards
The future of industry standards is likely to be defined by the increasing need for interoperability across diverse technologies and platforms. As systems become more interconnected, the importance of consistent standards will only grow. Standards will likely become even more sophisticated and adaptable to accommodate the complexities of emerging technologies. This adaptability will be critical in ensuring seamless integration and interoperability in the interconnected digital landscape.