The Rise of Mobile Devices
Mobile devices have become ubiquitous, transforming how we communicate, work, and access information. This widespread adoption has significantly broadened the attack surface for malicious actors, as these devices often lack the same robust security measures as traditional desktop computers. The increasing reliance on mobile platforms for sensitive data and financial transactions necessitates a heightened awareness of potential vulnerabilities. Moreover, the diverse range of mobile operating systems and applications further complicates security management and incident response.
The Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion
The proliferation of interconnected devices, forming the Internet of Things (IoT), has created a vast and complex network of potential entry points for cyberattacks. From smart home appliances to industrial control systems, these devices often have limited security features, making them vulnerable to exploitation. This interconnectedness creates a cascading effect, where a compromised IoT device can potentially compromise other networked systems. Securing this expanding ecosystem requires innovative approaches to security design and implementation.
Cloud Computing and Data Breaches
The shift to cloud-based services has revolutionized how businesses operate, offering scalability and accessibility. However, this transition also introduces new security challenges. Data breaches in cloud environments can have far-reaching consequences, impacting individuals and organizations alike. Cloud security relies heavily on robust access controls, encryption, and regular security audits to mitigate these risks. The increasing reliance on cloud-based infrastructure necessitates a shift in security mindset to focus on proactive measures rather than reactive responses.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap
The rapid evolution of the threat landscape is outpacing the development of cybersecurity skills and expertise. A significant gap exists between the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals and the available talent pool, leading to inadequate protection against sophisticated attacks. This shortage of qualified personnel poses a critical challenge for organizations of all sizes. Investing in cybersecurity education and training programs is crucial to address this gap and build a more resilient digital ecosystem.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring and Response
Cybersecurity is not a one-time fix; it's an ongoing process requiring continuous monitoring and proactive response mechanisms. Regular security assessments, vulnerability scanning, and incident response planning are essential to identify and address emerging threats effectively. Organizations must embrace a security-centric culture that prioritizes threat detection and mitigation. The ability to quickly identify and respond to security incidents is critical to minimizing damage and maintaining business continuity.
Malicious Software and Exploit Kits: A Constant Threat
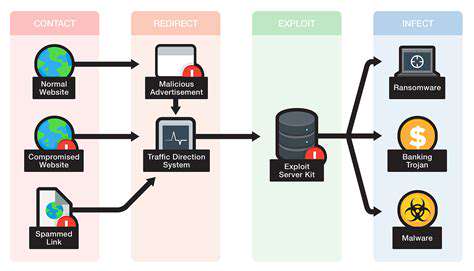
Malicious Software: A Deep Dive
Malicious software, often abbreviated as malware, encompasses a broad category of harmful programs designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems. These programs can range from simple viruses that replicate themselves to sophisticated spyware that steals sensitive information. Understanding the different types of malware is crucial to protecting your systems from attack. Malware can be disguised as legitimate software, making it difficult to identify without proper security measures in place.
Different types of malware have varying objectives. Some malware aims to simply disrupt system operations, while others seek to steal personal or financial data. Criminals can use this data for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious activities. Knowing the potential consequences of malware infection is essential for taking proactive steps to protect your digital assets.
Exploit Kits: The Delivery Mechanism
Exploit kits are sophisticated tools used by cybercriminals to deliver malware. They leverage vulnerabilities in software to gain unauthorized access to systems. These kits often contain a collection of exploits, each targeting a specific software flaw. The kits are frequently updated with new exploits, making them a serious threat to vulnerable systems.
The Connection Between Malware and Exploit Kits
Exploit kits are the primary delivery mechanism for malware. They act as a gateway for malicious programs to infect targeted systems. Cybercriminals use exploit kits to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in software, allowing them to install malware on unsuspecting users' computers. This process often happens automatically, making it difficult to detect and prevent.
The connection between these two components is critical. Exploit kits are the delivery system that gets malware onto your system. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing effective security strategies to defend against both exploit kits and the malware they deploy.
Protecting Yourself from Malware and Exploit Kits
Protecting yourself from malware and exploit kits requires a multi-layered approach. Regular software updates are vital, as they often patch vulnerabilities that exploit kits target. Using strong and unique passwords for all online accounts is another important step. Employing reputable antivirus and anti-malware software can also significantly reduce your risk.
Implementing robust security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, can add another layer of protection against malicious attacks. Furthermore, educating yourself about the latest threats and practicing safe online habits can significantly reduce your vulnerability. Staying informed and vigilant is essential to maintaining a secure digital presence.
Rooftop gardens, far from being purely aesthetic additions, can significantly boost a property's market value. Studies consistently demonstrate a positive correlation between green spaces and property appreciation. Potential buyers are increasingly drawn to homes featuring sustainable features and unique design elements, and a well-maintained rooftop garden certainly fits that bill. The visual appeal alone can elevate a property's perceived worth, but the practical benefits, such as enhanced curb appeal and a sense of community, further contribute to increased desirability and potentially higher sale prices. This is especially true in urban areas where green spaces are often limited, making a rooftop garden a desirable and valuable feature.
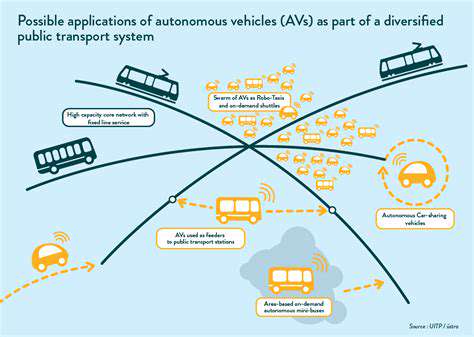
Countermeasures and Future-Proofing Connected Car Security
Strengthening Security Protocols
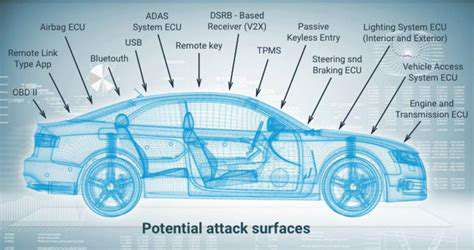
Modern connected cars rely on a complex network of interconnected systems, making them vulnerable to a wide array of cyberattacks. Robust security protocols are paramount to safeguarding this critical infrastructure. These protocols should encompass end-to-end encryption for all data transmissions, both within the vehicle and between the vehicle and external networks. Implementing multi-factor authentication for all access points, including those used by technicians and authorized personnel, is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of vehicle systems. This comprehensive approach to security will create a strong defense against potential threats and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential for proactive threat detection. These assessments should be conducted at all stages of vehicle development, from initial design to final deployment. The identification and subsequent remediation of vulnerabilities are critical to maintaining a high level of security. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and analysis of network traffic patterns can help in detecting and responding to suspicious activities in real-time. This proactive approach to security management will allow for rapid response to emerging threats and help maintain a high level of security in the face of evolving attack methods.
Implementing Advanced Security Technologies
Staying ahead of evolving cyber threats requires the integration of advanced security technologies. Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) within the vehicle's network architecture is a critical step in detecting and mitigating potential attacks. These systems can identify malicious activities in real-time, alerting security personnel to potential breaches and allowing for swift countermeasures. Additionally, the use of advanced encryption techniques, such as elliptic curve cryptography, can enhance the security of data transmitted between the vehicle and external systems, making it significantly more resistant to decryption attempts.
The development and implementation of robust security testing methodologies, including penetration testing and ethical hacking, are crucial to identify vulnerabilities in the system before malicious actors can exploit them. These simulated attacks allow security teams to evaluate the effectiveness of current security measures and identify areas for improvement. Continuous improvement in security protocols and technologies is essential to counter the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Furthermore, the development of tamper-resistant hardware and software solutions is critical to protecting the integrity of the vehicle's core functionalities. Using secure boot processes and hardware-based security modules can significantly reduce the risk of malicious code infiltration. This combination of advanced technologies will build a layered security approach, making connected cars considerably more resilient to cyberattacks.
Investing in ongoing research and development of novel security solutions is essential to anticipate and address future threats. Collaboration between automotive manufacturers, cybersecurity specialists, and research institutions can accelerate the development and deployment of advanced security technologies, ensuring that connected cars remain protected against emerging threats.