Grinding or Screeching Noises
One of the most common signs of failing wheel bearings is a noticeable grinding or screeching noise, particularly when the vehicle is turning or accelerating. This noise often intensifies as the bearing deteriorates further, becoming more pronounced and persistent. This sound is usually noticeable when the vehicle is moving and can vary in pitch and intensity depending on the severity of the damage. It's crucial to address this sound promptly as it can lead to further damage and potential safety hazards.
Vibration and Shaking
A significant vibration or shaking sensation emanating from the steering wheel, the vehicle's body, or the pedals can indicate a problem with the wheel bearings. This vibration is often more pronounced at higher speeds, as the spinning parts are under greater stress. The vibration often radiates through the vehicle, affecting the entire driving experience. This symptom can be mistaken for other issues, but a thorough inspection can pinpoint the problem.
Uneven Tire Wear
Failing wheel bearings can cause the tires to wear unevenly. You might notice a significant difference in the tread depth on one or more tires. This uneven wear pattern often shows up as a noticeably reduced tread on one side of the tire, and is a clear indication that something is amiss with the wheel assembly. This uneven wear can compromise the tire's grip and handling capabilities, making driving less stable and potentially dangerous.
Unusual Steering Wheel Play or Wobble
Noticeable play or wobble in the steering wheel, especially when the vehicle is moving, can suggest a problem with the wheel bearing. This play can be subtle at first, but it will worsen as the bearing deteriorates. This symptom is often associated with a grinding or screeching noise and may lead to loss of steering control. Inspecting the wheel bearings can confirm the cause of the issue.
Increased Vehicle Noise
In addition to the grinding or screeching sounds, a failing wheel bearing can lead to an overall increase in the vehicle's noise levels. This increase in noise might not be immediately associated with the wheel bearings, but it can often be a sign of damage. The increased noise can be more noticeable during acceleration and braking, and is a symptom that warrants immediate attention. This is a potential indication of a problem requiring professional repair to avoid further damage.
Difficulty in Turning or Steering
A failing wheel bearing can make it more difficult to turn the steering wheel or to maintain a consistent direction. This difficulty arises as the damaged bearing struggles to support the weight and movement of the wheel. This symptom can lead to loss of control, particularly at higher speeds. It is important to address this symptom promptly to prevent accidents and ensure safe driving conditions. Steering issues often accompany other warning signs and should not be ignored.
Wheel Bearing Maintenance and Replacement
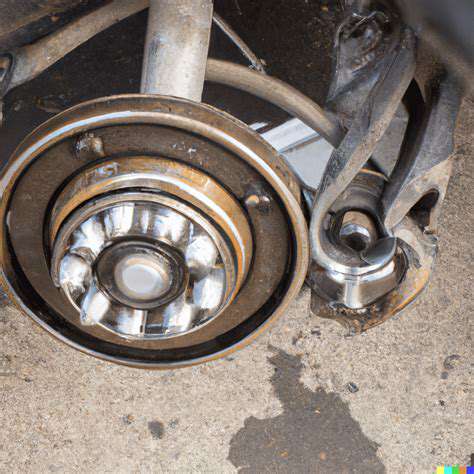

Wheel Bearing Inspection
Regularly inspecting your wheel bearings is crucial for preventing costly repairs down the line. Visual inspection is a good starting point, looking for any signs of excessive play or damage to the bearing housing or surrounding components. Pay attention to unusual noises, such as grinding or humming sounds, which can indicate internal bearing problems. A simple visual check can often reveal potential issues that may lead to catastrophic failure if left unaddressed.
Thorough inspection should involve checking for any signs of leaking grease or oil around the bearings. This could be a symptom of internal damage or a need for lubrication. Also, look for any signs of rust or corrosion, as these can compromise the bearing's structural integrity and lead to premature failure.
Frequency of Maintenance
The frequency of wheel bearing maintenance depends significantly on the type of vehicle, driving conditions, and the environment. For vehicles frequently driven on rough terrain or in harsh weather, more frequent checks are advised. Regular scheduled maintenance is essential to keep your vehicle running safely and efficiently.
Generally, wheel bearings should be inspected at every oil change or every 10,000 miles, whichever comes first. This will help to catch any emerging issues early and prevent them from escalating into more significant problems.
Tools and Equipment Needed
Having the right tools is essential for performing wheel bearing maintenance. You'll need a lug wrench, a socket set, and possibly a torque wrench, depending on the specific task. Specialized tools for bearing removal and installation may be necessary in some cases. Safety glasses and work gloves are also crucial for protecting yourself during the process. Proper lubrication is also necessary to keep the bearings functioning smoothly.
Grease and Lubrication
Proper lubrication is vital for the smooth operation and longevity of your wheel bearings. Using the correct type and amount of grease is critical for preventing friction and heat buildup, which can lead to damage. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual for specific recommendations on the type and amount of grease to use. Incorrect lubrication can significantly reduce the lifespan of the bearings.
Ensure the grease is applied evenly and completely around the bearing components. Excess grease can also be detrimental, so apply it judiciously and remove any excess to prevent issues.
Symptoms of Failing Bearings
Knowing the symptoms of failing wheel bearings can help you catch problems early. Common signs include unusual noises, such as grinding or humming sounds, vibration or shaking in the steering wheel or the whole vehicle, and a noticeable wobble in the wheel. These symptoms can worsen over time and lead to more serious issues.
If you detect these symptoms, it is important to address them promptly to prevent further damage. Ignoring these problems could lead to costly repairs or even safety risks.
Replacing Wheel Bearings
Replacing wheel bearings is a complex task that requires careful attention to detail. Proper removal and installation procedures are essential to ensure the bearings are properly seated and lubricated. It is highly recommended to seek professional assistance if you lack experience with this type of work. Incorrect installation can lead to premature failure of the bearing and potential vehicle damage.
Taking your vehicle to a qualified mechanic is strongly recommended for this type of work. They have the necessary tools, expertise, and safety precautions to ensure the job is done properly.
Safety Precautions
Safety should always be a top priority during any maintenance work, especially when dealing with wheel bearings. Always use appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and work gloves, to protect yourself from potential hazards. Ensure the vehicle is securely supported on jack stands or ramps before performing any work under the vehicle. This prevents the risk of the vehicle falling and causing injury.
Be mindful of the potential for loose parts and debris during disassembly. Taking precautions to prevent these hazards will ensure a safe and efficient maintenance process.
The Impact of Wheel Bearings on Vehicle Performance and Safety
Improved Vehicle Performance
Wheel bearings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient vehicle operation. Properly functioning bearings minimize friction between the wheel and axle, leading to reduced rolling resistance. This translates into improved fuel efficiency as the engine doesn't have to work as hard to propel the vehicle at a given speed. Furthermore, reduced friction contributes to a quieter ride, enhancing the overall driving experience. The seamless rotation provided by well-maintained bearings also allows for quicker acceleration and braking responses.
Consistent and precise bearing performance is essential for maintaining optimal vehicle handling. A smooth and predictable response from the steering and suspension systems directly correlates to the integrity of the wheel bearings. Without proper bearing function, the vehicle's handling can become unpredictable and potentially unsafe, particularly at higher speeds or during cornering maneuvers.
Enhanced Vehicle Safety
The safety implications of properly maintained wheel bearings are significant. Faulty bearings can lead to a loss of control, especially when driving at high speeds. Uneven or intermittent bearing wear can cause the wheel to wobble or pull to one side, making it difficult to maintain a straight path. This compromised stability directly increases the risk of accidents, especially in unpredictable road conditions or during maneuvers like lane changes.
Beyond the immediate threat of loss of control, faulty wheel bearings can damage other critical vehicle components. For instance, excessive bearing play can lead to premature wear and tear on the wheel hub, ultimately requiring costly repairs. In some cases, damaged bearings can even trigger a chain reaction of component failures, further increasing repair costs and potentially jeopardizing safety. Proper maintenance of wheel bearings is a crucial step in preventing such catastrophic failures.
Maintaining Bearing Integrity for Long-Term Reliability
Regular inspection and maintenance of wheel bearings are critical for ensuring their long-term integrity and reliability. This proactive approach not only prevents costly repairs but also contributes to the overall longevity of the vehicle. Scheduled maintenance, including visual inspections for signs of wear, unusual noises, or play in the wheel assembly, is vital for timely intervention and preventing potential issues from escalating.
Using the correct lubricants and grease specifications, as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer, is essential for maintaining optimal bearing performance. The lubrication process ensures that the bearings receive the necessary protection against friction, corrosion, and other damaging elements. By adhering to recommended maintenance schedules and using appropriate lubricants, vehicle owners can significantly extend the lifespan of their wheel bearings and contribute to the overall safety and reliability of their vehicles.