When Should You Replace Your Headlight Bulbs?

When to Replace Your Headlights
Replacing your headlights is a crucial aspect of vehicle maintenance, impacting your safety and visibility on the road. Regular inspections are essential to identify potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs down the line. Deteriorating headlights can lead to significant safety hazards, reducing your ability to see and be seen by other drivers, especially in low-light conditions. This can increase the risk of accidents and compromise your overall safety.
Several factors influence the need for headlight replacements. A gradual dimming of the light output, a yellowing or clouding of the lens, or a complete loss of light from a headlight are all clear indicators. Checking for cracks or damage to the housing is also vital, as this can compromise the integrity of the entire system and lead to increased risk. You should also consider the age of your vehicle, as older vehicles may require more frequent headlight replacements due to wear and tear.
Factors Affecting Headlight Replacement Frequency
The frequency of headlight replacements varies significantly depending on several factors. Driving conditions, such as frequent exposure to harsh weather, play a crucial role in the longevity of your headlights. For example, vehicles driven in climates with frequent snow, ice, or extreme temperatures are more likely to experience headlight damage sooner.
The quality of the headlights themselves matters. Some headlights are built to withstand harsh conditions better than others. Additionally, the driving habits of the owner play a part. Aggressive driving, including frequent hard braking and acceleration, can cause stress on components like headlights, potentially shortening their lifespan. Proper maintenance practices, such as regular cleaning and inspections, can significantly extend the life of your headlights.
Signs You Need New Headlights
Several noticeable signs indicate that your headlights might need replacement. A significant dimming or yellowing of the light output is a clear warning. This is often a result of internal components failing or the lens becoming damaged. This can make driving at night significantly more hazardous. A cloudy or cracked lens is another critical sign, as it reduces the light transmission and visibility.
Additionally, flickering or uneven light output is a potential indicator of a problem within the headlight unit itself. This could mean a faulty bulb, a wiring issue, or a problem with the headlight assembly. It is crucial to address these issues promptly to ensure safe driving conditions. If you notice any of these signs, schedule a visit to a qualified mechanic for proper diagnosis and replacement.
Different Bulb Types and Lifespan Variations
Incandescent Bulbs
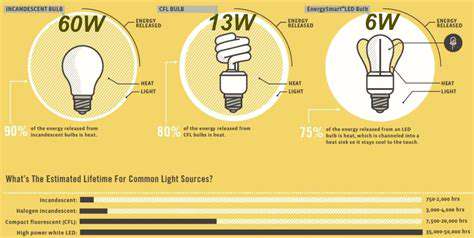
Incandescent bulbs, the classic light source, work by heating a thin filament inside a glass bulb until it glows. While they're familiar and inexpensive, they're not very energy-efficient, converting a significant portion of energy into heat rather than light. Their lifespan is generally shorter than other types, often lasting only a few thousand hours. This means more frequent replacements and a higher overall environmental impact compared to newer, more efficient technologies. Understanding their limitations is crucial for informed purchasing decisions.
The filament's heating process also produces a lot of heat, which can be a safety concern in certain applications. Careful consideration of the bulb's heat output is necessary when selecting a fixture or location for use. Choosing the right wattage for the intended use is also important to ensure the bulb operates safely and effectively. Furthermore, the short lifespan often leads to higher replacement costs over time.
Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs represent an improvement over incandescent bulbs, offering a slightly longer lifespan and higher efficiency. They use a halogen gas inside the bulb, which helps to maintain the filament and prolong its life. This allows for a brighter light output compared to standard incandescent bulbs, often with a similar warm-toned light. The increased efficiency often translates to a lower energy consumption compared to incandescents. However, they still produce a considerable amount of heat, which needs to be taken into account for installation.
Despite the improvements, halogen bulbs still aren't as energy-efficient as newer technologies like LEDs or CFLs. They are a step up from traditional incandescent bulbs, but they don't significantly reduce the environmental impact. The overall lifespan of halogen bulbs is typically in the range of 2,000 to 4,000 hours, which is still a considerable improvement over the lifespan of incandescent bulbs. Ultimately, the choice between halogen and incandescent bulbs depends on specific needs and priorities.
LED Bulbs
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for lighting due to their exceptional energy efficiency and long lifespan. Unlike incandescent bulbs that rely on heating a filament, LEDs use a semiconductor material to produce light. This significantly reduces energy consumption, resulting in substantial savings on energy bills over the long term. They produce a minimal amount of heat, making them safer and more suitable for various applications.
LED bulbs typically last tens of thousands of hours, often exceeding 50,000 hours. This translates to significantly fewer replacements and a lower environmental footprint. Their durability and longevity make them a cost-effective choice in the long run. Moreover, LEDs offer a wide range of color temperatures and brightness options, allowing for customization to match specific needs and preferences.
The initial cost of LED bulbs might be slightly higher than other types, but the long-term savings in energy and replacements quickly outweigh the initial investment. Their versatility and sustainability make them an excellent choice for both residential and commercial applications.
LED bulbs are also available in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and styles, allowing for seamless integration into existing fixtures and designs. Their compact nature makes them suitable for various applications, from home lighting to industrial settings. The superior efficiency and performance of LEDs make them a compelling option for any lighting need.
The environmental benefits are also notable. LEDs contain no harmful materials like mercury, which is a significant advantage over other types of bulbs. Their reduced energy consumption translates to a smaller carbon footprint.