Detecting impending wheel lock-up stands as the ABS's most crucial function. When braking forces overcome available traction, causing a wheel to stop rotating, the system springs into action. Wheel speed sensors provide the earliest possible warning of this dangerous condition.
Preserving Traction and Steering Response
By recognizing developing lock-up situations, the ABS modulates brake pressure to maintain optimal wheel rotation. This intervention preserves tire grip and, more importantly, allows the driver to maintain steering authority. Such control proves invaluable when attempting to avoid obstacles during emergency braking scenarios.
Safety Benefits of Wheel Speed Monitoring
The ABS's ability to respond to wheel speed variations provides measurable safety improvements. Statistics show these systems can reduce stopping distances by up to 30% on slippery surfaces while significantly lowering accident rates. This technology maintains vehicle stability even when drivers make panic stops or encounter unexpected road hazards.
These safety enhancements have made ABS technology virtually universal in modern vehicles, saving countless lives since its widespread adoption.
ABS Sensor Varieties and Their Operations
Wheel Speed Detection Mechanisms
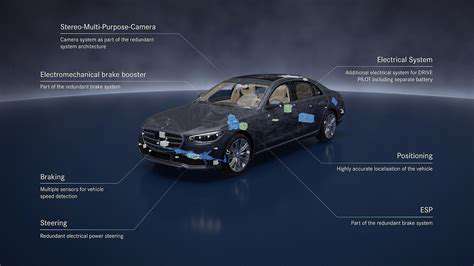
Modern ABS systems employ several sensor technologies to monitor wheel rotation. The most common design uses a toothed ring and magnetic pickup to generate alternating current signals corresponding to wheel speed. Engineers typically mount these sensors in wheel hubs where they can precisely track rotational movement without mechanical contact.
The system's control module analyzes these signals hundreds of times per second, watching for abnormal deceleration patterns that might indicate impending lock-up. This constant vigilance allows for intervention before traction loss becomes irreversible.
Rotational Velocity Measurement
Some advanced systems utilize Hall-effect sensors for even greater precision in measuring angular velocity. These solid-state devices offer improved reliability and accuracy compared to traditional magnetic designs. Their digital output provides cleaner signals that are less susceptible to electrical interference.
Position Awareness Systems
Integrated position sensors complement speed data by tracking wheel orientation. While not directly measuring velocity, this information helps the ABS understand wheel behavior in three-dimensional space. Such data proves particularly valuable during cornering maneuvers when wheels rotate at different speeds.
This positional awareness enhances the system's ability to predict and prevent loss of control during complex driving situations. The technology has become increasingly sophisticated with the introduction of active safety systems like electronic stability control.
Hydraulic System Monitoring
Pressure sensors in the brake lines provide critical feedback about force application. These components work in concert with wheel speed sensors to create a comprehensive picture of braking dynamics. The ABS uses this combined data to precisely modulate hydraulic pressure at each wheel.
Modern systems can make these adjustments dozens of times per second, far faster than any human driver could manage. This capability explains why ABS-equipped vehicles often stop shorter while maintaining better control than those without it.
Recognizing and Diagnosing ABS Sensor Issues
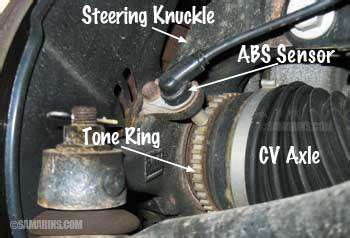
Sensor Function Fundamentals
ABS sensors represent a critical link in modern vehicle safety systems. By constantly monitoring wheel behavior, they enable the computer to prevent dangerous lock-up situations. Even minor sensor malfunctions can compromise the entire system's effectiveness, making prompt diagnosis essential.
These components face constant exposure to road debris, temperature extremes, and vibration - all factors that can lead to premature failure. Technicians must understand both electronic and mechanical failure modes to properly service these systems.
Recognizing Fault Symptoms
Drivers might notice several warning signs when ABS sensors begin failing. The most obvious is illumination of the ABS warning lamp, though some systems may trigger the check engine light instead. More subtle symptoms include unusual pedal feedback or inconsistent braking performance during hard stops.
In severe cases, drivers may experience complete ABS deactivation, often accompanied by conventional brake system operation. While the vehicle remains drivable, its emergency stopping capability becomes significantly compromised.
Diagnostic Approaches
Modern scan tools provide technicians with direct access to ABS sensor data streams. These diagnostic instruments can reveal intermittent faults that might not trigger warning lights while providing valuable historical performance data. Many professional-grade scanners can even simulate sensor inputs to verify system responses.
Physical inspection remains equally important, as damaged wiring or corroded connectors often cause sensor-related issues. Technicians should examine the entire signal path from sensor to control module when troubleshooting.
Electrical Connection Inspection
Signal integrity depends on clean, secure electrical connections throughout the system. Corrosion at connector points represents one of the most common causes of ABS sensor failures, particularly in regions using road salt during winter months. Proper cleaning and dielectric grease application can often restore normal operation.
Physical Sensor Examination
Direct visual inspection can reveal physical damage from road hazards or improper servicing. Technicians should check for cracked sensor bodies, damaged mounting points, or excessive play in rotating components. Even minor physical damage can significantly affect sensor accuracy and reliability.
Data Interpretation Techniques
Understanding sensor output patterns requires both technical knowledge and experience. Professional technicians compare live data from all wheels while driving at various speeds to identify discrepancies. This approach helps distinguish between sensor failures and mechanical issues like worn wheel bearings that might affect readings.
Considering System-Wide Factors
While sensors themselves fail frequently, technicians must consider broader system issues. Problems with the ABS pump, module, or even the vehicle's main computer can mimic sensor failures. A comprehensive diagnostic approach that examines all potential failure points ensures accurate repairs and prevents unnecessary part replacement.