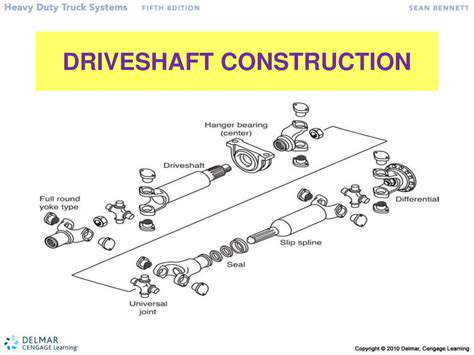
A Deeper Dive into the Ethical Dilemma
The trolley problem, a thought experiment in ethics, forces us to confront difficult choices with severe consequences. It's a powerful tool for exploring our moral reasoning and the complex interplay between different ethical frameworks, from utilitarianism to deontology. Understanding the nuances of this problem allows us to better analyze real-world ethical dilemmas.
This seemingly simple scenario, with its stark choices, highlights the profound impact of our decisions on others. It compels us to consider the potential ramifications of our actions and the often-uncomfortable trade-offs inherent in ethical decision-making.
Utilitarianism and the Trolley Problem
Utilitarianism, a prominent ethical theory, argues that the best action is the one that maximizes overall happiness and well-being. Applying utilitarianism to the trolley problem often leads to the conclusion that sacrificing one life to save five is the morally correct choice, prioritizing the greater good. This approach, while seemingly logical, raises important questions about the inherent value of individual lives.
However, a crucial criticism of utilitarianism in this context is its potential to devalue individual lives. The calculation of happiness and suffering can feel cold and impersonal, potentially leading to justifying morally questionable actions in the name of greater overall benefit.
Deontological Perspectives on the Trolley Problem
In contrast to utilitarianism, deontological ethics emphasizes moral duties and rules. Deontologists might argue that intentionally causing harm to one person, even to save others, is inherently wrong, regardless of the consequences. This perspective often leads to a rejection of the trolley problem's central choice, emphasizing the importance of upholding moral principles even in the face of difficult circumstances.
A core principle of deontology is respect for persons, meaning that individuals should never be treated as mere means to an end. This principle, if applied to the trolley problem, suggests that sacrificing one person to save others violates the inherent worth and dignity of the individual.
The Role of Intentions in Ethical Decision-Making
The trolley problem forces us to consider the role of intentions in ethical decision-making. Is the act of pulling a lever to divert the trolley morally equivalent to pushing a person in front of the trolley to stop it? The difference in intentions, even if the outcome is the same, might be seen as a crucial factor in evaluating the ethical implications of each action.
The Trolley Problem's Relevance to Modern Society
While a theoretical exercise, the trolley problem resonates deeply with modern societal challenges. From resource allocation in healthcare to debates about autonomous vehicles, ethical dilemmas demanding difficult choices are pervasive. Examining these scenarios through the lens of the trolley problem can provide valuable insights into how we approach complex ethical questions in our daily lives.
Understanding the different perspectives presented by the trolley problem can help us develop more nuanced and thoughtful approaches to these issues, moving beyond simplistic answers and embracing a deeper understanding of the moral considerations involved.
Liability and Responsibility in Autonomous Driving Incidents
Defining Liability
Establishing clear lines of liability in autonomous driving incidents is paramount. This necessitates a comprehensive framework that considers the various actors involved, including the vehicle manufacturer, the software developer, the owner of the vehicle, and the passengers. Determining who bears responsibility for damages in the event of an accident requires careful analysis, factoring in the degree of human intervention, the specific circumstances of the incident, and the functionality of the autonomous system at the time of the event. This intricate web of potential liabilities requires careful legal and ethical scrutiny to ensure fairness and accountability.
The Role of Human Oversight
Autonomous vehicles, while aiming for complete self-sufficiency, often rely on human oversight and intervention. The degree of human control and the specific protocols governing that control significantly influence liability. In accidents involving a mix of human and autonomous decision-making, apportioning responsibility becomes a complex legal challenge. Should the driver be held liable for failing to properly monitor the system, or should the manufacturer be responsible for inadequacies in the autonomous driving software?
The extent of human interaction with the vehicle’s autonomous functions, and the protocols governing that interaction, directly impact the allocation of blame in the event of an incident. This dynamic interplay between human and machine necessitates clear guidelines and regulations to ensure that responsibility is fairly and transparently assigned.
Manufacturer Responsibility
Vehicle manufacturers play a crucial role in the ethical landscape of autonomous driving. Their responsibility extends beyond the physical design of the vehicle to encompass the development, testing, and maintenance of the autonomous driving software. A manufacturer's failure to adequately test or maintain the software, or to address known safety vulnerabilities, could lead to significant liability in the event of an accident. Ensuring the safety and reliability of the autonomous driving systems is a critical responsibility that must be met with rigorous standards and accountability.
Passenger Responsibility
Passengers in autonomous vehicles also hold a degree of responsibility, although it's often less direct than that of the driver in traditional vehicles. Passengers should be aware of the limitations of the autonomous system and understand the safety protocols in place. Failing to heed safety warnings or engage in disruptive behavior that affects the autonomous system's functioning could potentially affect the allocation of responsibility in an accident. Education and clear communication about passenger responsibilities are crucial in mitigating potential liability concerns.
Ethical Considerations in Algorithm Design
The algorithms governing autonomous vehicles are the heart of the technology, and their design has profound ethical implications. Ethical dilemmas can arise when algorithms must make split-second decisions in complex or unpredictable situations. For example, how should the algorithm prioritize the safety of pedestrians versus the safety of passengers? The ethical frameworks that inform the design of these algorithms need careful consideration, ensuring they are robust enough to address the full spectrum of potential scenarios and that they are transparent and understandable. The long-term implications of different algorithmic choices on liability and public trust need careful evaluation.
Public Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Establishing clear and comprehensive public policy and regulatory frameworks is essential for managing the complexities of autonomous driving liability. These frameworks should address issues such as data privacy, vehicle safety standards, and the responsibility of various stakeholders. Governments must play a vital role in creating a predictable legal environment that encourages innovation while simultaneously protecting the safety of the public. Developing a regulatory framework that keeps pace with technological advancements and addresses the unique challenges of autonomous vehicles is essential for fostering public trust and ensuring responsible innovation.
Privacy Concerns and Data Security in Self-Driving Cars
Data Collection and Storage
Self-driving cars rely heavily on data collection for their operation, gathering information from various sensors, cameras, and radar systems. This data, which includes location data, images, and even audio recordings, raises significant privacy concerns. The sheer volume of data collected, combined with its potential sensitivity, necessitates robust data security measures to protect individuals from unauthorized access and misuse. Ensuring that this data is collected and stored ethically and responsibly is crucial for maintaining public trust in this emerging technology.
The potential for misuse of this data is considerable. Imagine a scenario where a self-driving car's onboard cameras record sensitive information about a person's daily routine, including interactions with family or friends, or even potentially private conversations. Protecting this data from unauthorized access and ensuring its secure storage is paramount.
Potential for Surveillance
The extensive use of sensors and cameras in self-driving cars raises concerns about potential surveillance capabilities. The ability to record and potentially analyze everything around the vehicle could give rise to concerns about privacy violations and the misuse of this data for purposes beyond the intended functionality of the vehicle. This is a particular concern as the technology develops and expands its capabilities.
Careful consideration must be given to the types of data collected, the duration of data storage, and the specific circumstances under which the data might be accessed. Transparency and clear guidelines are essential to maintain public trust and prevent misuse of the collected information.
Data Security Breaches
As with any technology involving sensitive data, self-driving cars are vulnerable to security breaches. Hackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the vehicle's systems to access and manipulate the data collected, potentially leading to serious consequences. The implications of a data breach could range from minor inconveniences to significant risks to personal safety.
Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to mitigate these risks. These measures should include encryption, secure data storage protocols, and regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Continuous monitoring and updates to the systems are also crucial to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Liability and Accountability
Determining liability in the event of a data breach or misuse of information collected by self-driving cars is a complex legal and ethical challenge. Questions arise regarding who is responsible for the protection of the data and who is accountable for any resulting harm.
Ethical Considerations in Data Use
The ethical implications of data use in self-driving cars extend beyond privacy concerns. Questions arise about how the collected data might be used to discriminate against certain groups or individuals. For example, biases in the data could lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in the vehicle's decision-making processes.
Careful consideration must be given to ensure that the data collection and use practices are fair and equitable, avoiding any potential for bias or discrimination. This requires careful design, rigorous testing, and ongoing evaluation of the systems to identify and address any potential issues.
Transparency and User Control
Transparency and user control over the data collected by self-driving cars are critical to building public trust. Clear and accessible policies regarding data collection, storage, and use are essential. Users should have the ability to understand how their data is being used and have some control over its usage.
Providing users with options for data deletion or opting-out of certain data collection practices is crucial. This fosters a sense of empowerment and allows individuals to make informed decisions about their personal data in the context of self-driving vehicles.