Addressing Construction Site Safety
Construction zones present inherent dangers, requiring proactive strategies to minimize risks and protect personnel. Developing thorough safety measures from initial planning to project completion is absolutely essential. These measures encompass routine safety evaluations, supplying appropriate protective gear, and cultivating a workplace culture where safety awareness is prioritized by everyone involved.
Mandatory safety training programs must be regularly refreshed to account for new hazards and evolving best practices. This forward-thinking safety strategy not only decreases accident probabilities but also promotes a more efficient and conscientious work atmosphere, yielding benefits for the entire project.
Importance of Risk Assessment
Comprehensive risk evaluations are vital for spotting potential dangers and creating appropriate control methods. These evaluations should examine every project element, from materials selected to work procedures implemented. Early hazard detection enables the creation of focused safety approaches to reduce accident risks.
An extensive risk analysis must account for possible falls, equipment failures, and contact with dangerous substances. By predicting these potential issues, construction firms can establish preventive actions and define explicit safety protocols to lower accident probabilities.
Implementing Effective Safety Protocols
Applying strong safety measures throughout all project phases is critical for worker protection. This includes unambiguous communication of safety rules, holding frequent safety meetings, and guaranteeing proper utilization of safety gear. Creating transparent communication pathways between management and workers is fundamental for an effective safety initiative.
Construction firms must verify that all employees comprehend and follow safety procedures. This involves providing continuous instruction and enforcing established protocols. Periodic examinations and assessments of safety measures are required to pinpoint improvement areas and maintain ongoing adherence.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Complete emergency readiness plans are necessary for reducing the effects of unexpected incidents at construction sites. These plans should detail processes for managing various emergency situations, including fires, medical crises, and natural calamities. Setting up clear communication methods and assigning specific emergency roles is crucial for prompt and efficient responses.
Worker Training and Education
Committing to extensive employee instruction and education programs represents a key element of construction site safety. Regular training should address multiple subjects, including hazard identification, safe work methods, and correct use of protective equipment. Practical training on particular tasks and machinery ensures workers are adequately prepared and proficient in performing their jobs safely.
Beyond the Algorithm: Addressing Public Concerns Regarding Data Privacy and Security
Data Collection Practices: Transparency and Consent
Understanding data gathering, usage, and sharing processes is fundamental for establishing public confidence. Transparent data collection approaches, including plain explanations about collected data, its purpose, and intended applications, are imperative. This requires moving from obscure procedures toward an inclusive model where individuals actively participate in decisions about their information. Additionally, securing informed consent is critical, ensuring people comprehend data sharing consequences and can modify or withdraw consent when desired.
Creating effective systems for obtaining and managing consent is vital. These systems should be straightforward, understandable, and available to all users, regardless of technical knowledge. Plain language combined with simple opt-out choices forms the foundation of a reliable data collection framework.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Algorithms inherently learn from data. When training data reflects existing social prejudices, these algorithms may reinforce and potentially intensify such biases. This can result in unjust or discriminatory consequences, particularly affecting marginalized communities. Consequently, it's crucial to examine potential biases in training data and actively assess algorithms for impartiality and justice.
Stringent review and testing processes are required to detect and reduce algorithmic bias. This necessitates incorporating diverse viewpoints during development and evaluation stages, guaranteeing thorough comprehension of possible effects across different population segments. Continuous observation and algorithm modifications are necessary to maintain fairness and equity over time.
Data Security and Protection
Safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, misuse, exposure, modification, or destruction is critical. Strong protective measures, including encryption, access restrictions, and periodic security evaluations, are fundamental for data protection. Establishing secure data storage and transfer methods is equally important, as is formulating and executing clear breach response strategies. This involves active efforts to identify and resolve potential security weaknesses.
Data protection represents an ongoing commitment rather than a single occurrence. Regular security protocol updates, employee education on protection best practices, and implementing advanced security technologies all contribute to sustaining a secure data environment. Moreover, clear user communication regarding data security policies is essential.
Accountability and Oversight Mechanisms
Defining clear responsibility boundaries for data handling practices is fundamental. This includes appointing specific individuals or entities accountable for adherence to data protection laws and ethical standards. Creating independent monitoring organizations to examine data practices and address complaints can further strengthen accountability.
Openness in data management practices and enabling individuals to contest decisions or report issues constitute key aspects of accountability. Systems must exist to promptly and effectively handle user concerns and complaints. This involves providing accessible feedback and resolution channels.
The Role of Regulation and Policy
Governments bear significant responsibility in establishing and upholding data privacy laws. These regulations should be extensive, encompassing the complete data lifecycle from collection to deletion. They must also remain flexible to accommodate technological advancements and changing societal requirements. Precise, straightforward guidelines and standards for data management across various industries are necessary to guarantee uniform and proper execution.
Successful implementation of privacy regulations demands rigorous enforcement procedures. Violation penalties should be substantial enough to discourage non-compliance and promote responsible data handling. International collaboration and standardization of privacy laws are also crucial given the global nature of data movement.
Public Awareness and Education
Increasing public understanding of data privacy and security matters is imperative. Educational programs, including workshops, training sessions, and digital materials, can equip individuals with knowledge and skills to safeguard their information. This includes comprehending their rights under privacy legislation and learning how to make informed data-related choices.
The Future of Data: Ethical Considerations
As data assumes growing importance in daily life, examining the long-term ethical consequences of its use becomes vital. This includes investigating potential data misuse, effects on personal autonomy, and the necessity for continuous discussion and cooperation among stakeholders. Anticipating possible societal impacts of future data applications is essential.
Continuous interaction with ethical principles and standards is paramount. This involves assessing potential prejudice, discrimination, and harm possibilities while actively seeking mitigation methods. Ongoing conversation and partnership among researchers, regulators, and the public are required to ensure proper and ethical data practices.
The Human Element: Redefining the Driver Experience and Public Expectations
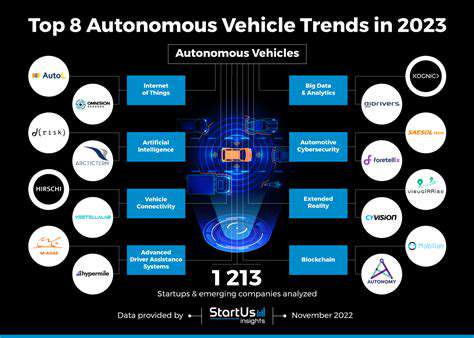
Autonomous Vehicles and the Shifting Role of the Driver
The emergence of self-driving vehicles is fundamentally transforming the driving experience, moving away from conventional human control models. This transition requires reassessing public assumptions about safety, accountability, and the very concept of driving. As automation increases, human involvement in transportation evolves from active operation to a more observational, monitoring function. This fundamental change raises complicated questions about liability, trust, and the changing dynamic between humans and technology in personal transportation.
Public Perception and Acceptance of Autonomous Vehicles
Widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles depends heavily on public approval. Public opinion forms through numerous influences, including safety worries, ethical questions about accidents, and potential economic effects on current transport sectors. Informing the public about the technology and alleviating their concerns is crucial for creating a favorable environment for autonomous transportation's future. Honesty and clear information sharing are vital for establishing confidence and overcoming doubts.
Ethical Considerations in Autonomous Driving
Self-driving vehicles introduce complex moral questions. How should unavoidable accident situations be handled? Who bears responsibility when autonomous cars are accident-involved? Programming systems to make instantaneous decisions during emergencies presents substantial ethical difficulties. Creating guidelines and structures for ethical decision-making in autonomous vehicles is necessary to ensure responsible and fair implementation of this technology.
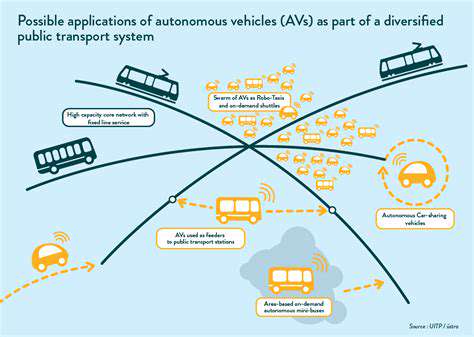
The Impact on Transportation Infrastructure and Urban Planning
Broad acceptance of self-driving vehicles will probably require substantial adjustments to transport systems. Current roads, parking facilities, and public transit networks might need redesigning to meet autonomous vehicles' special needs. City planning must adapt to potential improvements in traffic efficiency and alterations in commuting behaviors. Evaluating effects on urban regions and existing transport networks is critical for successfully incorporating autonomous vehicles into society.
Economic Impacts and Job Displacement
The growth of autonomous vehicles could transform multiple industries, including freight transport, ride-hailing, and taxi services. This transformation will create significant economic consequences, possibly causing employment reductions in these fields. Adjusting to these changes demands proactive steps to assist affected workers, encourage new job prospects, and ensure an orderly economic transition. Predicting these potential effects and developing workforce adaptation plans are essential for navigating this new economic reality.
The Future of Personal Mobility and Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles might transform personal transportation, providing extraordinary access for people with disabilities, senior citizens, and those lacking conventional transport options. By eliminating driver's license requirements or personal vehicle ownership needs, self-driving cars could dramatically improve accessibility and quality of life for many. Additionally, enhanced mobility options and customized transport solutions present fresh opportunities for city development and community planning.