Understanding the Expanding Digital Footprint
Modern technology has transformed how we interact with devices, leading to a rapidly growing attack surface for cybercriminals. This shift is driven by the surge in networked gadgets, software, and online services, each potentially harboring security flaws. The convenience of connectivity comes at a cost, as it simultaneously creates more entry points for malicious activities. Grasping the nuances of this digital expansion is vital for implementing proper safeguards.
What began with basic personal computers has evolved into intricate IoT ecosystems in homes and workplaces. The sheer quantity of linked devices now forms an attractive playground for hackers aiming to steal confidential information or sabotage essential operations.
The Cloud Computing Security Paradox
While cloud solutions have transformed business operations through flexible scaling and cost efficiency, they've introduced novel security dilemmas. Companies frequently transfer security obligations to cloud providers, potentially creating intricate and vulnerable setups. Navigating cloud security demands deep familiarity with provider-specific protections and a holistic defensive framework within the cloud space.
Maintaining data confidentiality and accuracy in cloud platforms while benefiting from their scalability remains an ongoing challenge. This necessitates meticulous attention to authorization protocols, information scrambling methods, and routine security evaluations.
Mobile Devices and the BYOD Challenge
The mobile revolution, coupled with Bring Your Own Device policies, has complicated security landscapes significantly. Personal gadgets accessing corporate networks create fragmented protection scenarios, potentially exposing sensitive business information to device-level weaknesses.
Countering mobile and BYOD security threats demands comprehensive solutions. Deploying advanced mobile management tools, establishing stringent security standards, and conducting regular employee training on mobile protection strategies are all crucial components.
Internet of Things Security Gaps
IoT technology has brought remarkable convenience by linking everything from household appliances to industrial equipment. However, this interconnectivity comes with substantial security shortcomings. Many IoT products have minimal processing capabilities and basic security features, leaving them open to digital intrusion. The prevalence of inadequate security standards in IoT devices presents serious dangers to both consumers and enterprises.
The possibility of large-scale operational disruptions and data compromises originating from IoT weaknesses is becoming increasingly alarming. Protective measures must be applied at both device and network levels to reduce these hazards.
Supply Chain Security Complexities
Modern supply networks involve numerous vendors and partners, creating potential security weak points. A single vulnerable link could jeopardize the entire chain. Assessing and managing security across all supply chain participants is absolutely essential. This involves detailed evaluations, periodic security checks, and comprehensive agreements that clearly define security obligations.
A successful supply chain security strategy must be forward-looking, extending well beyond an organization's direct activities. Developing trust and cooperation with all partners is fundamental for spotting and neutralizing possible threats.
Software Vulnerabilities Persist
Application weaknesses continue to pose constant dangers. Hackers frequently target these flaws to gain illegal system access. Keeping software updated with the latest security patches remains critical for reducing these risks.
Creating and maintaining secure applications is an ongoing process. Implementing safe programming techniques, exhaustive testing procedures, and regular vulnerability assessments form the foundation of a solid application security plan.
Exploitation Methods and Potential Impacts
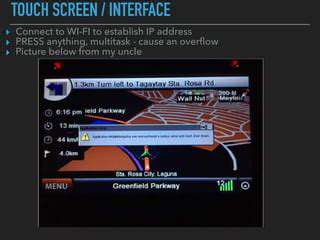
Infotainment System Vulnerabilities
Automotive entertainment systems, despite their convenience features, contain multiple security gaps. Their internet connectivity makes them susceptible to various attack methods. Common issues include poorly secured interfaces, obsolete software components, and weak authentication processes. Cybercriminals can leverage these deficiencies to infiltrate systems, potentially accessing private information, manipulating vehicle operations, or interrupting normal functionality.
An additional serious consideration is the possibility of remote system takeover. Such access could enable data theft, conversation monitoring, or even vehicle control interference. The extensive data flow between vehicles and external servers creates numerous attack possibilities for skilled hackers.
Vehicle Functionality Risks
Successful infotainment system breaches can have severe consequences for vehicle operations. Attackers might gain command over crucial components like braking mechanisms, steering systems, or engine controls. This could result in dangerous malfunctions, including control loss, collisions, or complete operational failure. These threats become particularly concerning during emergency scenarios where reliable vehicle performance is essential.
Beyond direct safety issues, compromised entertainment systems can interfere with other vehicle functions. Consider situations where hackers remotely disable navigation, climate controls, or audio systems. While initially appearing as minor inconveniences, these disruptions could escalate into more serious safety concerns.
Occupant Safety Considerations
Passenger security remains paramount, and infotainment system vulnerabilities present genuine dangers. Attackers manipulating critical vehicle operations such as braking or steering creates immediate safety hazards, potentially leading to accidents or worse. The possibility of remote vehicle function interference highlights the urgent need for comprehensive cybersecurity protections.
Data Privacy Challenges
Connected vehicle systems gather extensive personal information including location history, online activity, and user preferences. System breaches could expose this sensitive data, leading to identity fraud, financial crimes, or other privacy violations. The potential for misuse of personal information collected through these platforms represents a major concern requiring careful attention.
The continuous data exchange between vehicles and external servers demands strong security measures and encryption standards to prevent unauthorized access. Safeguarding this information is vital for maintaining user privacy and preventing personal data exploitation.
Security Best Practices
Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures is crucial for reducing infotainment system risks. This includes adopting strong authentication methods, consistent software updates, and advanced threat detection systems. Detailed security evaluations and penetration testing can identify weaknesses and inform defensive strategies.
Additionally, educating vehicle users about potential risks and promoting secure usage habits can significantly decrease exploitation likelihood. Clear communication about data practices and security implementations plays a key role in building user confidence.
The Future of Cybersecurity in the Automotive Industry

Changing Threat Environment
Digital security threats continue to advance, with attackers refining their methods to exploit vulnerabilities. Ranging from infrastructure-targeting ransomware to complex phishing schemes aimed at organizations and individuals, today's threat environment is unprecedentedly dynamic. This demands proactive, adaptable security approaches requiring constant attention and advanced technologies to maintain protection.
Artificial Intelligence's Growing Role
AI is becoming increasingly important in cybersecurity operations. Intelligent systems can process enormous datasets to detect threat patterns and anomalies, enabling quicker threat identification and response. AI automation handles numerous security tasks, allowing human experts to concentrate on strategic challenges. This capability is essential for managing the overwhelming volume of modern digital threats.
The Zero Trust Approach
Traditional perimeter-based security models no longer suffice in today's interconnected environment. The zero trust framework, which assumes no inherent trust regardless of user or location, is gaining prominence. This method validates every access attempt to resources, whether originating inside or outside organizational networks. Adopting zero trust principles represents a significant strategic shift but provides superior protection for sensitive systems and information.
Cloud Security Implications
While cloud technology has revolutionized business operations, it introduces distinct security considerations. Organizations must guarantee proper cloud security implementation, including strict access management and data encryption. Cloud data protection requires combined traditional and cloud-specific security solutions for comprehensive coverage. Modern cloud environments demand more integrated and proactive security approaches than ever before.
Advanced Data Protection Needs
Information breaches remain a top concern for businesses of all scales. Securing sensitive data necessitates complete strategies incorporating encryption, access restrictions, and regular security reviews. Comprehensive data protection plans are fundamental for reducing breach risks and preventing unauthorized data access. Data compromise consequences can range from financial impacts to significant reputation damage.
Human Factors in Security
Despite technological advancements, human involvement remains critical in cybersecurity. Staff training and awareness initiatives are vital for threat recognition and response. Educating employees about phishing attempts, social engineering ploys, and common attack methods is essential for developing strong security awareness. Effective training programs help minimize human mistakes that frequently enable successful cyberattacks.