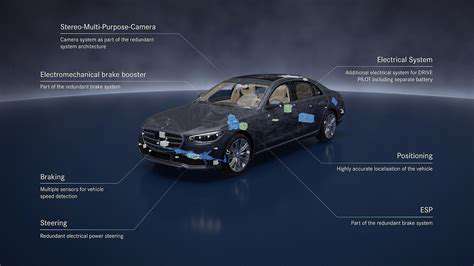
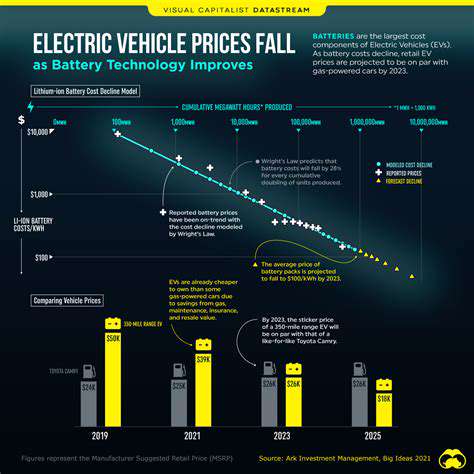
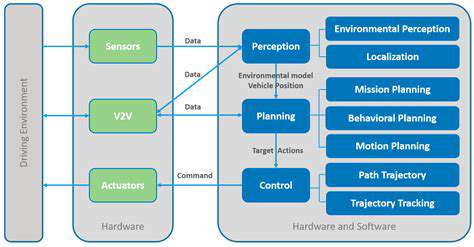
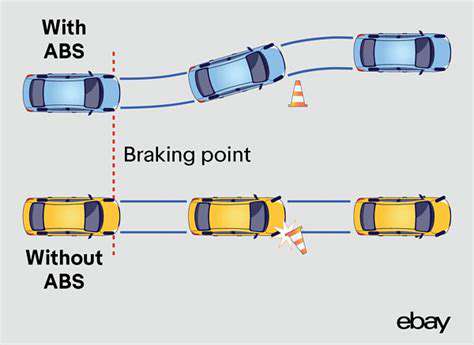
Data Security and Potential for Malicious Use
Data Integrity and Protection
Ensuring data remains unaltered and secure is a cornerstone of modern systems, particularly when dealing with sensitive information. Data integrity guarantees accuracy, completeness, and consistency from creation to deletion. Without proper safeguards, unauthorized changes, accidental errors, or deliberate attacks can undermine trust in critical processes.
Modern security protocols like end-to-end encryption, role-based access permissions, and automated backup systems form the frontline defense against digital threats. These technologies not only prevent unauthorized access but also guarantee data availability during emergencies.
Threats from Malicious Software
As digital transformation accelerates, organizations face growing risks from sophisticated malware and viruses. These harmful programs can corrupt databases, disrupt operations, and expose confidential records. Security teams must implement multi-layered defense systems that evolve alongside emerging threats.
Advanced endpoint protection, next-generation firewalls, and behavior-based detection tools have become indispensable. Continuous security updates and real-time monitoring provide dynamic protection against constantly changing attack vectors.
Strategic Access Management
Proper access governance significantly reduces exposure to internal and external security breaches. Implementing granular permission structures based on job requirements creates essential barriers against data compromise. This principle of least privilege limits potential damage from both accidental and intentional misuse.
Mitigating Human Factors
Employee mistakes represent one of the most persistent vulnerabilities in security systems. Common errors like falling for phishing scams or mishandling sensitive files can have severe repercussions. Continuous security education transforms staff from potential liabilities into active defense assets.
Interactive training sessions combined with clear security protocols help employees recognize and avoid risks. This investment in human capital creates an organizational culture where security becomes second nature.
Regulatory Compliance Imperatives
Organizations handling sensitive data must navigate complex regulatory landscapes including HIPAA and GDPR. These frameworks establish mandatory protections and carry significant penalties for non-compliance. Proactive compliance demonstrates organizational maturity and builds stakeholder confidence.
Regular compliance audits and gap assessments ensure security measures meet evolving regulatory requirements. Documentation of these processes provides evidence of due diligence during regulatory reviews.
Liability and Accountability in Autonomous Vehicle Accidents

Legal Responsibility Framework
Auditors face significant legal exposure when professional standards aren't met. This exposure ranges from inadequate risk assessment to failure in detecting material misstatements. Mastering jurisdiction-specific legal requirements is fundamental to managing professional liability. Comprehensive knowledge of auditing standards provides the foundation for risk mitigation.
Potential legal actions may arise from financial statement errors impacting investors or undetected fraudulent activities. Meticulous work documentation serves as critical evidence of professional diligence when defending against claims.
Professional Accountability Standards
Auditors must uphold rigorous professional standards through transparent processes and ethical conduct. This includes comprehensive documentation and unbiased reporting. The profession's credibility depends on unwavering commitment to ethical principles. Such commitment fosters essential trust in financial systems.
Evaluating and documenting internal control effectiveness represents a core accountability requirement. These assessments must clearly identify weaknesses while suggesting practical improvements.
Regulatory Compliance Landscape
Diverse legal frameworks govern auditing practices across different markets and industries. These structures ensure financial reporting quality while defining auditor responsibilities. Navigating this complex landscape requires specialized legal and technical expertise.
Professional auditing standards provide detailed methodologies for conducting effective audits. Strict adherence to these guidelines maintains the profession's integrity and value.
Comprehensive Risk Evaluation
Thorough risk assessment forms the backbone of effective auditing. This process requires careful examination of financial records, operational procedures, and control environments. Auditors must balance professional skepticism with practical business understanding.
Documentation Best Practices
Detailed audit documentation provides crucial protection against liability claims. These records must comprehensively capture procedures, findings, and conclusions. Complete documentation supports audit quality and defends against negligence allegations.
Evidence collection requires strategic planning to ensure appropriate quality and quantity. The audit team must carefully select evidence types and collection timing to support reliable conclusions.
Effective Stakeholder Communication
Audit reports must clearly convey findings using accessible language tailored to various stakeholders. Precise communication ensures users can make fully informed decisions based on audit results. The report should transparently present the audit opinion and any significant concerns.
Ongoing dialogue with management regarding control deficiencies and reporting practices enhances audit effectiveness. This collaborative approach improves financial reporting quality.
The Need for Transparency and User Control

Data Collection Transparency
Modern digital experiences require complete clarity about user data practices. Clear disclosure of collected data, its purposes, and sharing practices establishes essential user trust. Opaque data policies can permanently damage customer relationships and brand reputation.
Accessible privacy notices should use plain language to explain specific data types collected and their business applications. Users deserve straightforward information about location tracking, preference analysis, and advertising uses.
User-Focused Design Philosophy
Successful products emerge from deep understanding of user needs and behaviors. Investing in user research and iterative testing creates experiences that genuinely resonate with target audiences. This human-centered approach drives engagement and satisfaction.
Multi-Channel User Support
Providing diverse support options caters to varying user preferences and needs. Comprehensive support systems including live chat, email, and phone assistance demonstrate commitment to user success. Well-organized knowledge bases and FAQs enable efficient self-service solutions.
Multiple contact channels ensure all users can access help through their preferred medium. This flexibility significantly improves overall satisfaction and reduces frustration.
Ethical Data Stewardship
Organizations must clearly communicate their data protection measures and incident response capabilities. Transparent security practices demonstrate serious commitment to safeguarding user information. Ethical data handling builds confidence and differentiates responsible businesses.
Privacy protection requires ongoing attention to regulatory changes and industry best practices. Ethical considerations should guide all data-related decisions.
Trust-Based Relationships
Transparent operations and respectful data practices cultivate lasting user relationships. When companies prioritize user empowerment, they benefit from increased loyalty and advocacy. This trust becomes a competitive advantage in crowded markets.
Inclusive Design Approach
Accessible design considers the full spectrum of human diversity and ability. Implementing universal design principles ensures equal access for users with varying needs and preferences. True inclusivity moves beyond compliance to create genuinely welcoming experiences.
Multilingual support and adaptive interfaces demonstrate commitment to serving diverse populations. Inclusive design ultimately benefits all users through improved usability and flexibility.