Developing Robust Safety Protocols and Regulatory Frameworks
Ensuring Safety Through Comprehensive Protocols
Developing robust safety protocols is paramount in the ethical design of any system, particularly those with potential for widespread impact. These protocols must be meticulously crafted to anticipate potential hazards and mitigate risks before they manifest. They should encompass a range of scenarios, from standard operating procedures to contingency plans for unexpected events. Thorough testing and validation of these protocols are crucial to ensure their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This process should involve diverse perspectives and input from stakeholders to ensure comprehensiveness and address potential biases or blind spots.
A strong emphasis on proactive safety measures, rather than simply reactive responses, is essential. Predictive modeling and risk assessment tools can aid in identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing preventative strategies. This proactive approach fosters a culture of safety, where individuals are empowered to identify and report potential risks, ultimately contributing to a more secure and reliable system.
Establishing Clear Regulatory Frameworks
Alongside robust protocols, clear regulatory frameworks are essential to govern the deployment and operation of any system. These frameworks must be transparent, easily accessible, and consistently enforced. They need to be adaptable to evolving technologies and societal needs, ensuring they remain relevant and effective over time. Regulations should not stifle innovation but rather guide its responsible application.
Clear definitions of responsibilities and accountability are paramount within these frameworks. This includes establishing mechanisms for reporting incidents, conducting investigations, and implementing corrective actions. Furthermore, provisions for public scrutiny and participation in the regulatory process can foster trust and transparency, ultimately strengthening the integrity and ethical soundness of the system.
Addressing Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
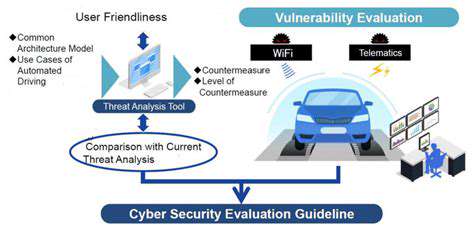
Proactive identification and assessment of potential risks and vulnerabilities are critical components of any safety program. This involves careful consideration of the entire system lifecycle, from design and development to deployment and maintenance. Identifying potential misuse or unintended consequences is crucial. This necessitates a multifaceted approach that incorporates various perspectives, including those of users, developers, and independent security experts.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify weaknesses in the system's defenses. These assessments should be conducted throughout the system's lifespan, allowing for timely adjustments and improvements to mitigate emerging risks. Thorough documentation of vulnerabilities and the actions taken to address them is crucial for continuous improvement and knowledge sharing within the field.
Promoting Ethical Considerations in Safety Design
Ethical considerations should permeate every stage of safety protocol and regulatory framework development. This encompasses fairness, equity, and the minimization of harm to all stakeholders. Ethical guidelines need to be explicitly incorporated into the design process, ensuring that safety measures are not disproportionately impacting certain groups. Considerations of privacy, data security, and algorithmic bias must be central to these protocols and regulations.
Promoting open communication and collaboration among stakeholders, including affected communities, is essential to ensure the ethical implications of safety measures are carefully considered. Transparent documentation and justification for safety decisions will build trust and foster greater acceptance of the systems being developed and implemented. This commitment to ethical considerations is critical for building public trust and ensuring long-term sustainability.