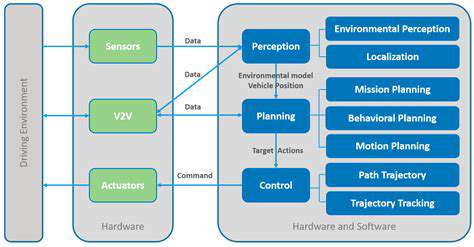
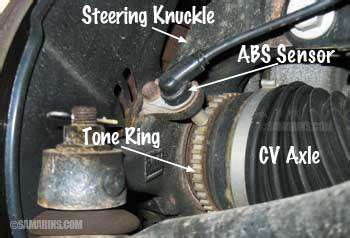
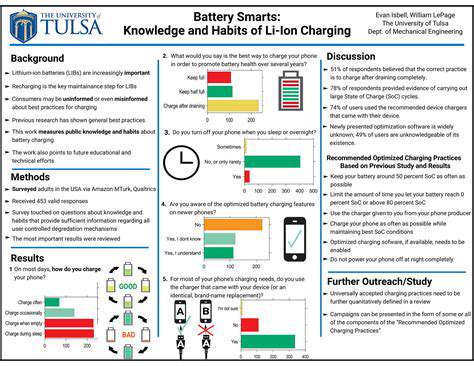
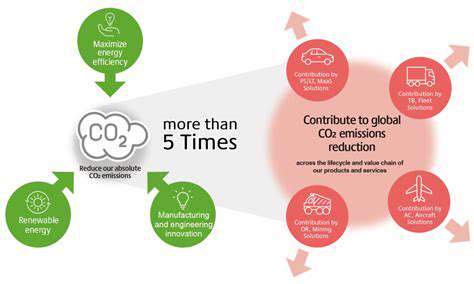
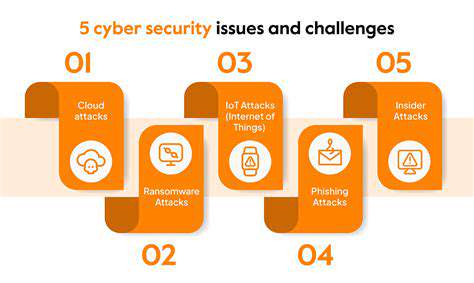
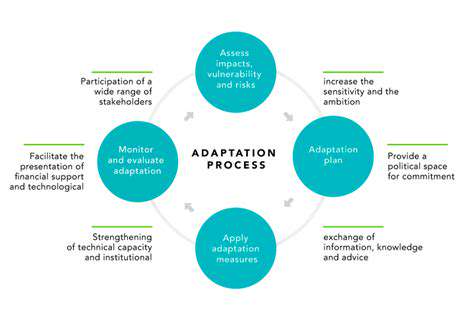
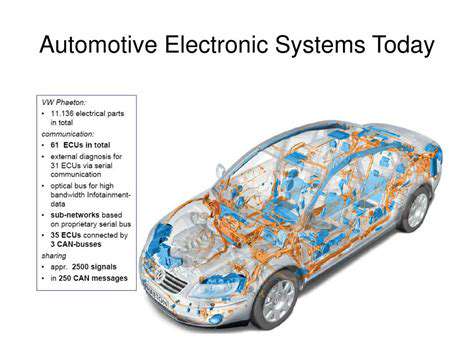
Redundancy, in its simplest form, is the inclusion of extra components or processes to ensure continued functionality even if some parts fail. This concept is crucial in various systems, from critical infrastructure to everyday technology. The ability of a system to maintain operation in the face of failure is paramount, and redundancy plays a vital role in achieving this resilience.
Modern systems, particularly those handling sensitive data or critical tasks, often rely heavily on redundant components. This approach mitigates risks associated with single points of failure and enhances the system's overall reliability. Implementing redundancy can significantly reduce downtime and improve the overall performance of the system.
Types of Redundancy
Redundancy manifests in diverse forms, encompassing hardware duplication, software backups, and even personnel duplication in certain roles. Hardware redundancy involves having multiple identical components, such as power supplies or processors, ready to take over if the primary component fails.
Software redundancy typically involves maintaining multiple copies of critical software or data, enabling recovery from software errors or data corruption. This strategy is particularly valuable in preventing data loss and ensuring business continuity.
Furthermore, redundancy can extend to personnel, particularly in critical roles. Having multiple individuals with the same level of expertise in place provides a safety net and ensures that knowledge and skills are not lost in case of personnel issues.
Benefits of Redundancy
The benefits of implementing redundancy are considerable, ranging from enhanced system reliability to improved business continuity. Redundancy minimizes the risk of system failures, leading to a significant reduction in downtime and associated costs. This approach translates to increased productivity and efficiency for the organization.
Moreover, redundancy safeguards sensitive data and prevents disruptions in critical operations. This is especially crucial in industries where data integrity and operational continuity are paramount, such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications. The overall stability and security of systems are greatly enhanced.
Cost Considerations of Redundancy
While redundancy offers substantial benefits, it does involve additional costs. The expenses associated with implementing redundancy can vary significantly depending on the type and scope of the system being protected.
These costs often include the purchase and maintenance of additional components, specialized personnel, and training. Careful planning and cost-benefit analysis are essential in evaluating the viability of implementing redundancy measures.
Redundancy and Disaster Recovery
Redundancy plays a critical role in disaster recovery plans. By having backup systems and data copies, organizations can quickly restore operations after a disaster or unexpected event. This preparedness ensures minimal disruption to business activities and allows for a swift return to normal operations.
Furthermore, having redundant systems in place during disasters can prevent data loss, which is a critical concern in many industries. The ability to quickly recover from disasters is crucial for maintaining business continuity and minimizing the negative impacts of unforeseen events.
Implementing Redundancy Strategies
Implementing effective redundancy strategies requires careful planning and execution. A thorough assessment of potential risks and vulnerabilities is essential. This includes identifying critical components and processes and designing backup systems to ensure their continued operation during failures.
Regular testing and maintenance of redundant systems are crucial to ensure their operability and effectiveness. This includes rigorous testing procedures to verify that backup systems can successfully take over when needed, and ongoing maintenance to keep everything in optimal working order.
The Importance of Human-Machine Interface Design

The Synergy of Human and Machine
The convergence of human intelligence and machine capabilities is revolutionizing industries and reshaping our daily lives. This intricate interplay, often referred to as human-machine interaction, fosters innovation and efficiency in unprecedented ways. The ability to leverage the strengths of both humans and machines allows for a more holistic and effective approach to problem-solving, leading to remarkable advancements across diverse fields.
Harnessing the power of machines frees human potential to focus on tasks requiring creativity, critical thinking, and complex judgment. This synergy allows for the development of innovative solutions and strategies that were previously unimaginable.
Augmented Capabilities Through Collaboration
Human-machine interaction is not about replacing humans; rather, it's about augmenting human capabilities. Machines excel at repetitive tasks, data analysis, and processing vast amounts of information with speed and accuracy. By integrating these capabilities into human workflows, we can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency across various sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare.
This collaborative approach allows professionals to dedicate more time to higher-level tasks, strategic decision-making, and relationship building, ultimately leading to a more satisfying and fulfilling work experience.
Enhanced Decision-Making Processes
Machines provide valuable insights and data-driven recommendations that can inform human decision-making. By analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, machines can uncover hidden correlations and potential risks that might otherwise go unnoticed. This data-driven approach can significantly improve the accuracy and effectiveness of decisions, leading to better outcomes.
By integrating machine learning algorithms and sophisticated analytical tools, organizations can make better, more informed decisions, leading to increased profitability and success. This process also allows for a more transparent and accountable decision-making process, as the reasoning behind choices can be clearly articulated and validated.
Improving Accuracy and Consistency
One of the most significant benefits of human-machine collaboration is the potential to improve accuracy and consistency in various processes. Machines can perform tasks with unparalleled precision and repeatability, reducing errors and improving overall quality. This is particularly valuable in industries where accuracy is critical, such as manufacturing, medicine, and finance.
From meticulously precise manufacturing processes to the accurate diagnosis of complex medical conditions, human-machine interaction holds the key to a more precise and reliable future. This enhanced accuracy translates into improved outcomes and greater confidence in the results obtained, driving innovation and progress across numerous sectors.
Ethical Considerations and Future Implications
As human-machine interaction evolves, it's essential to address the ethical considerations that arise. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and job displacement must be carefully considered and addressed to ensure responsible and equitable development and implementation of these technologies.
The future of human-machine interaction promises exciting possibilities, but also presents challenges. Open discussions and thoughtful consideration of the ethical implications are crucial to ensuring that this powerful technology is used for the betterment of humanity and society as a whole.
Furthermore, understanding the nuanced ways in which humans and machines can complement each other will be critical to unlocking the full potential of this powerful collaboration.