Autonomous Navigation: Sensors and Perception
Autonomous navigation systems rely heavily on sophisticated sensor technologies to perceive and interpret their environment. These sensors, acting as the eyes and ears of the vehicle, collect data about the surrounding world, including distances, objects, and other relevant information. Accurate and reliable sensor data is crucial for the system's ability to make safe and effective decisions. This data is processed by complex algorithms that translate raw sensor inputs into a meaningful understanding of the environment, allowing the vehicle to identify obstacles, map its surroundings, and plan its route accordingly.
Different types of sensors are employed, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) provides highly accurate 3D point clouds, enabling the system to create detailed maps and detect obstacles with precision. Cameras provide visual information, offering a wide field of view and the ability to recognize objects and road markings. Radar sensors contribute to the system's understanding of the environment by detecting objects at varying distances and speeds, supplementing the information from cameras and lidar. Integrating data from multiple sensor types is essential for robust and reliable perception, improving the system's overall performance and safety.
Planning and Control: Algorithms and Strategies
Once the autonomous vehicle has a comprehensive understanding of its environment through sensor data processing, it needs a robust plan to navigate safely and efficiently. This involves creating a path from the starting point to the destination, while taking into account obstacles, traffic rules, and real-time changes in the environment. Complex algorithms are crucial for calculating optimal paths, considering factors like speed limits, lane markings, and other vehicles on the road.
The system must also be able to execute the planned path in a safe and controlled manner. This involves precise control of the vehicle's movement, including steering, acceleration, and braking. Advanced control algorithms, often based on reinforcement learning or model predictive control, allow the vehicle to adapt to dynamic situations and make necessary adjustments to maintain the intended trajectory. These algorithms are constantly evaluated and refined to improve the vehicle's responsiveness and stability in various driving conditions. Furthermore, the system needs to be able to handle unexpected events, such as sudden changes in traffic or pedestrian behavior, demonstrating its adaptability and resilience.
The combination of sophisticated planning and control algorithms is essential for the successful operation of autonomous navigation systems, enabling them to react to and manage complex situations in real-time.
The ability to make rapid and accurate decisions based on the ever-changing environment is paramount to safe autonomous navigation.
GPS Enhancement Techniques for Autonomous Vehicles
Improving GPS Accuracy
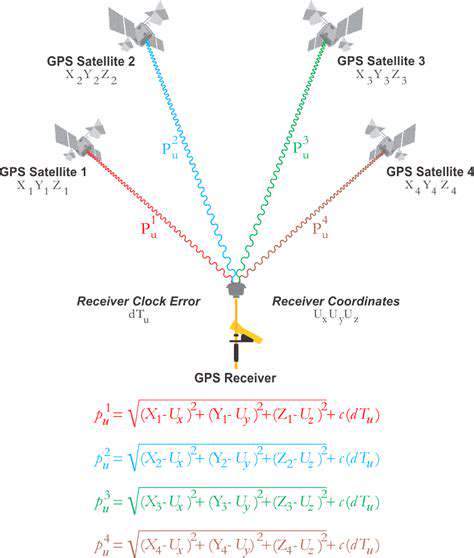
GPS signals, while generally accurate, can be susceptible to interference and multipath effects. These issues can lead to significant inaccuracies in positioning data, potentially endangering autonomous vehicles. Techniques to mitigate these problems include using multiple GPS satellites, employing differential GPS (DGPS) which utilizes reference stations to correct for errors, and incorporating signal processing algorithms to better identify and eliminate corrupted signals. These methods enhance the reliability and precision of GPS data, a critical component for safe and effective autonomous vehicle operation.
Sophisticated signal processing algorithms are crucial for filtering out noise and interference. These algorithms analyze the incoming GPS signals, identify potential errors, and adjust the positioning data accordingly. This refined signal processing plays a key role in improving the accuracy of the GPS data, enabling autonomous vehicles to navigate with greater precision and confidence.
Utilizing Complementary Sensors
GPS systems, while highly effective, are not immune to all potential errors. To enhance reliability and safety, autonomous vehicles often incorporate complementary sensor technologies. These include inertial measurement units (IMUs) that measure acceleration and angular velocity and cameras or lidar systems that provide visual and depth information. Combining GPS data with IMU and sensor data allows for a more robust and accurate positioning system, especially in challenging environments like dense urban areas or under heavy foliage.
By integrating data from multiple sources, autonomous vehicles can create a more comprehensive understanding of their surroundings and their position within it. This integrated approach helps to compensate for GPS inaccuracies and ensure accurate and safe navigation, particularly in complex or dynamic environments.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS is a high-precision technique that significantly improves the accuracy of GPS positioning. RTK GPS utilizes a network of reference stations to provide real-time corrections to the user's GPS receiver. This results in centimeter-level accuracy, which is crucial for precise autonomous vehicle navigation and positioning, especially in applications requiring high-level accuracy like autonomous construction or delivery robots.
Utilizing Assisted GPS (A-GPS)
Assisted GPS (A-GPS) technology enhances the speed at which a GPS receiver acquires a fix. A-GPS works by pre-downloading satellite ephemeris data to the receiver, reducing the time required to acquire signals and determine location. This is particularly beneficial in situations where rapid localization is crucial, such as in dynamic traffic environments or during emergency maneuvers. This technology is vital for rapid response and efficient operation in autonomous vehicles.
By pre-loading data, A-GPS significantly reduces the time it takes to establish a GPS fix compared to traditional GPS systems. This faster acquisition time is essential for autonomous vehicle applications where immediate location awareness is necessary for safe and efficient operation.
Challenges and Future Directions
While significant progress has been made in GPS enhancement techniques, challenges remain. Factors such as signal jamming, atmospheric interference, and the limitations of current sensor technology present obstacles to achieving perfect GPS accuracy. Future research focuses on developing more resilient GPS receivers, exploring new sensor integration strategies, and investigating novel signal processing techniques to address these challenges and further enhance the performance of GPS systems in autonomous vehicles.
The development of advanced signal processing algorithms and the use of more sophisticated sensor fusion techniques will continue to play a key role in improving the accuracy and reliability of GPS systems in autonomous vehicles. Further research is necessary to mitigate the impact of GPS signal degradation in challenging environments and to create a more robust and adaptable system for autonomous navigation.
The Role of GPS in Autonomous Vehicle Safety
Accurate and reliable GPS positioning is fundamental to the safety of autonomous vehicles. GPS data provides the essential framework for navigation, path planning, and obstacle avoidance. Robust GPS enhancement techniques, including the integration of complementary sensors and advanced signal processing, are crucial in ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles in various driving scenarios. Without accurate positioning, autonomous vehicles cannot reliably navigate and respond to unexpected situations, which could lead to accidents or other hazardous outcomes.
The seamless integration of GPS with other advanced technologies directly impacts the safety of autonomous vehicles. This integration enables the vehicle to make informed decisions based on real-time environmental data, enhancing its ability to respond appropriately to unforeseen circumstances. Accurate and reliable GPS is the cornerstone of this advanced safety system.
The Integration of GPS with Other Sensors

GPS Integration with Navigation Systems
Integrating GPS technology with navigation systems has revolutionized how we navigate. This integration allows for real-time location tracking and precise directions, eliminating the need for paper maps and cumbersome route planning. The GPS signal provides the foundation for sophisticated mapping software, enabling users to access detailed information about points of interest, traffic conditions, and alternative routes.
GPS in Vehicle Tracking and Management
In the realm of fleet management and logistics, GPS plays a crucial role in tracking and managing vehicles. Real-time vehicle location data helps optimize routes, monitor driver performance, and ensure timely delivery. This data is vital for businesses to stay organized, reduce operational costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Furthermore, GPS integration allows for remote monitoring of vehicle health and maintenance needs.
GPS Integration for Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture leverages GPS technology to optimize farming practices. GPS-guided equipment can precisely apply fertilizers, pesticides, and water, minimizing waste and maximizing crop yields. This technology also enables farmers to track field conditions and monitor crop growth in real time, leading to more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
GPS in Mapping and Surveying
GPS technology is fundamental to modern mapping and surveying. Its accuracy and precision allow for the creation of detailed maps and the surveying of large areas, which is vital for infrastructure projects, land management, and environmental studies. These maps offer an in-depth visualization of the Earth's surface, facilitating efficient planning and decision-making.
GPS Integration in Emergency Response
In emergency response situations, GPS plays a critical role in locating and responding to incidents. First responders can use GPS-enabled devices to pinpoint the precise location of accidents, medical emergencies, or other critical events. This precise location data is essential for dispatching resources quickly and efficiently. The integration of GPS with communication systems further enhances the effectiveness of emergency response teams.
GPS in Personal Navigation and Outdoor Activities
For personal navigation and outdoor activities, GPS has become an indispensable tool. Portable GPS devices provide accurate location information, enabling hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts to navigate challenging terrains and track their progress. Moreover, GPS allows users to locate themselves in unfamiliar areas, ensuring they don't get lost. These devices facilitate outdoor adventures and enhance safety by providing real-time location data.