Redefining Residential Aesthetics
Interior design is more than just arranging furniture; it's about crafting a space that reflects your personality and lifestyle. A well-designed interior can significantly impact your mood and overall well-being. Considering the interplay of light, color, and texture is crucial in creating a truly immersive and personalized experience. Designing spaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing is a primary goal for interior designers.
Modern trends often favor open-concept layouts, maximizing natural light and creating a sense of spaciousness. However, the integration of traditional elements can add warmth and character to a contemporary aesthetic. The careful selection of materials, from flooring to fabrics, contributes significantly to the overall ambiance of the space. Sustainable and ethically sourced materials are gaining popularity, reflecting a growing awareness of environmental consciousness in interior design.
Embracing Functionality and Creativity
A thoughtfully designed interior prioritizes functionality and usability. Every element, from lighting fixtures to storage solutions, should serve a purpose and enhance the overall flow of the space. This includes careful consideration of traffic patterns and the placement of furniture to facilitate easy movement and interaction.
Beyond functionality, interior design offers a platform for creative expression. Personalizing the space with unique artwork, carefully selected accessories, and meaningful personal items can transform a home into a truly unique and cherished sanctuary. By embracing creative solutions, homeowners can create a space that reflects their individual style and lifestyle, making it a comfortable and inspiring environment.
The incorporation of technology into interior design is also evolving rapidly. Smart home features, integrated entertainment systems, and interactive displays are seamlessly blending technology into everyday life, offering both functionality and aesthetic appeal. The use of smart lighting systems and automated blinds can further enhance the comfort and efficiency of a space.
Integrating technology seamlessly into the design is key to creating a modern and practical environment. The challenge lies in finding the right balance between innovation and aesthetics to avoid a jarring clash of technology and design.
Creating a visually appealing space goes beyond simply choosing the right colors and materials. It requires a deep understanding of the interplay between form, function, and personal expression. Interior design is a dynamic field, constantly evolving to meet the needs and aspirations of homeowners. This requires designers to remain adaptable and creative to cater to the ever-changing trends and preferences of clients.
Exterior Aesthetics: Beyond Function to Form and Flow
Sculpting the Silhouette: Aerodynamic Design and Visual Impact
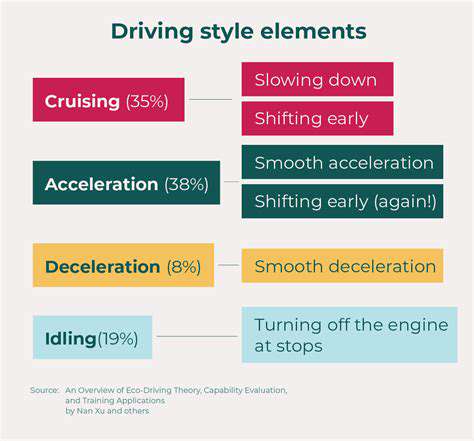
Modern automotive design is increasingly focused on creating vehicles that are not only functional but also visually captivating. The sleek, aerodynamic silhouettes of many contemporary models are a testament to this trend. Careful consideration of airflow, minimizing drag, and maximizing downforce contribute to improved fuel efficiency and handling. At the same time, these aerodynamic principles are translated into compelling shapes, lines, and curves that speak to the driver's aesthetic sensibilities. This fusion of form and function is key to creating vehicles that are both desirable and efficient.
The evolution of exterior design is heavily influenced by computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Sophisticated software allows designers to simulate airflow around a vehicle model, identifying areas for improvement and optimizing the shape for maximum performance and efficiency. This integration of technology allows for a beautiful and functional design to be achieved simultaneously.
Material Innovation: Sustainable and Striking Surfaces
The materials used in exterior panels are undergoing a significant transformation. Manufacturers are increasingly exploring sustainable alternatives to traditional materials like steel and aluminum. This is a move driven by environmental concerns and the desire for lighter, stronger components. For instance, composites are gaining traction for their potential to reduce weight and offer unique design possibilities. Expect to see a rise in innovative materials that are not only environmentally friendly but also capable of producing striking visual effects.
Color and Light: Dynamic Visuals and Emotional Responses
Color and light play a crucial role in shaping the overall aesthetic of a vehicle. Modern design emphasizes the interplay between different hues, textures, and light reflections. Advanced paint technologies allow for intricate color gradients, metallic finishes, and unique optical effects. These elements contribute to the vehicle's visual appeal and evoke different emotional responses in the viewer. The way light interacts with the surface of a car can significantly alter its perceived aesthetics and contribute to its overall appeal.
Integrated Lighting Systems: Signature Illuminations and Enhanced Safety
Exterior lighting is evolving from basic functional components to dynamic design elements. Integrated LED lighting systems offer unparalleled flexibility in terms of shape, intensity, and color. Manufacturers are using these systems to create distinctive signatures, enhancing the vehicle's visual appeal at night and signaling the vehicle's identity. Moreover, these systems are designed not just for aesthetics but also for enhanced safety, improving visibility and driver awareness.
Interactive Surfaces and Textures: Tactile Experiences and Enhanced Design
The exterior surfaces are no longer just for aesthetics; they are becoming interactive and responsive. Innovative textures and materials can be integrated into the design, providing a unique tactile experience for the driver and passengers. This extends beyond the visual and into the realm of sensory engagement. The integration of advanced materials and technologies allows for a more immersive and personalized driving experience.
Window and Glass Integration: Transparency and Visual Connectivity
The role of windows and glass in automotive design is changing. Manufacturers are experimenting with new glass technologies, offering improved visibility and a seamless connection between the interior and exterior. This trend is driven by the desire for a more spacious and airy interior, while also maximizing driver visibility. The strategic use of glass and glazing can transform the overall feel and perception of a vehicle, influencing the driver's connection with the surrounding environment.
The Future of Exterior Design: Beyond the Visual
The future of automotive exterior design extends beyond the visual. It incorporates technological advancements, sustainability considerations, and a deeper understanding of the emotional connection between the driver and the vehicle. Exterior design is increasingly focused on creating vehicles that are not only beautiful but also efficient, sustainable, and capable of enhancing the driving experience in meaningful ways. The evolution of exterior design will likely continue to intertwine form and function, pushing the boundaries of both visual appeal and performance.
Safety and Security: Design Considerations for a Driverless World
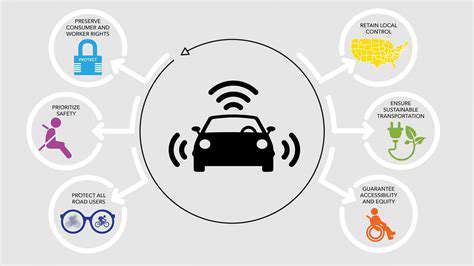
Safety Features for Enhanced Security
Implementing robust safety features is crucial for ensuring a secure environment. These features should be thoughtfully integrated into the design process, rather than as an afterthought. Prioritizing user safety should be paramount, and this includes designing for potential hazards and vulnerabilities. Careful consideration of potential threats and vulnerabilities is essential to proactively mitigate risks and safeguard users. This proactive approach helps to prevent accidents and incidents, and fosters a sense of trust and confidence in the system.
One key aspect of safety design involves incorporating fail-safe mechanisms. These mechanisms are designed to automatically revert to a safe state in case of an unexpected event or malfunction. For example, systems with fail-safe mechanisms can automatically shut down power or stop a process in the event of a critical error. This proactive approach to safety can significantly reduce the potential for harm and ensure a stable and reliable experience for all users. The implementation of fail-safe mechanisms is critical to ensure the system's stability and reliability.
Security Protocols and Measures
Robust security protocols are essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. These protocols should be comprehensive and cover various aspects of data handling, including transmission, storage, and access control. Implementing strong authentication methods is vital to verify the identity of users and prevent unauthorized access to critical information. This ensures the integrity and confidentiality of data, safeguarding against malicious actors.
Data encryption plays a critical role in securing sensitive information. Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches. This is a critical component of overall security strategy, and should be considered in the design phase. Implementing encryption protocols protects sensitive information from interception or unauthorized modification. This is a fundamental aspect of any security-conscious design.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical to identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities in the system. These assessments should be conducted periodically to ensure that the security measures remain effective and up-to-date. Ongoing monitoring and maintenance of security measures are necessary to address any potential threats. These proactive measures contribute significantly to the overall security posture of the system.
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security for user accounts. This approach requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, making it much harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access. MFA significantly enhances security and strengthens the system's defenses against unauthorized access.
The Future of Mobility: Integrating Design with Urban Planning
Sustainable Transportation Solutions
The future of mobility hinges on innovative solutions that prioritize sustainability. This means moving beyond the limitations of traditional vehicles and embracing alternative transportation methods. Electric vehicles, while a step in the right direction, need to be integrated into a broader ecosystem of sustainable practices, including efficient charging infrastructure and the development of renewable energy sources to power them. Furthermore, promoting cycling and walking through dedicated infrastructure and creating more accessible public transportation networks are crucial for reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality in urban environments.
Cities must actively encourage and support these sustainable options to foster a more environmentally conscious and healthy urban landscape. This includes incentives for purchasing electric vehicles, substantial investments in public transportation, and the creation of dedicated bike lanes and pedestrian zones.
Urban Design and Mobility Integration
Urban design plays a critical role in shaping the future of mobility. Smart city initiatives that incorporate real-time traffic data, intelligent traffic management systems, and optimized public transportation routes are essential for creating efficient and accessible transportation networks. This will not only reduce congestion but also improve travel times and enhance the overall quality of life for city residents. The integration of design principles into urban planning ensures that transportation infrastructure is not just functional but also aesthetically pleasing, enhancing the overall urban experience.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Mobility
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the way we think about and experience mobility. Autonomous vehicles, ride-sharing services, and connected transportation systems are rapidly transforming the landscape of urban transportation. These technologies promise to improve efficiency, safety, and accessibility, but their implementation must be carefully considered to ensure equitable access and avoid exacerbating existing inequalities. Careful planning and regulation are crucial to navigate the ethical implications of these technological advancements and ensure their responsible deployment.
The Impact of Autonomous Vehicles on Urban Spaces
The emergence of autonomous vehicles has the potential to significantly alter urban spaces. Reduced reliance on personal vehicles could lead to the repurposing of parking lots, the creation of more pedestrian-friendly zones, and the redevelopment of streets for enhanced public spaces. However, the transition to autonomous vehicles also presents challenges, such as the need for specialized infrastructure and the potential displacement of jobs in the transportation sector. Careful consideration of these impacts will be crucial for successfully integrating autonomous vehicles into urban environments.
The Future of Public Transportation Systems
Public transportation systems are vital components of any sustainable mobility strategy. Modernizing these systems through investments in advanced technologies, enhanced connectivity, and improved accessibility will be essential for integrating them seamlessly into the overall urban landscape. This includes not only expanding existing routes but also integrating diverse forms of transportation, such as bike-sharing programs and ride-sharing services, into a unified network. Furthermore, the integration of real-time data and user-friendly apps will improve the user experience and encourage wider adoption of public transit.
Addressing Equity and Accessibility in Mobility
Ensuring equitable access to mobility for all members of society is paramount in shaping the future of urban planning. This includes addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as individuals with disabilities, low-income communities, and the elderly. Transportation systems must be designed to be accessible and affordable, regardless of socioeconomic status or physical limitations. This means incorporating universal design principles, providing affordable transportation options, and creating supportive infrastructure that caters to the diverse needs of all citizens.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Design for a Greener Future

Sustainable Practices in Industrial Processes
Implementing sustainable practices in industrial processes is crucial for mitigating environmental impact and ensuring long-term viability. Companies are increasingly recognizing the need to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt environmentally friendly technologies. This involves careful consideration of resource consumption, waste generation, and emissions throughout the entire production cycle. From sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and disposal, each stage presents opportunities for improvement and optimization. Sustainable practices can encompass a wide range of strategies, including the use of renewable energy sources, waste reduction and recycling initiatives, and the development of cleaner production methods. Adopting these practices can lead to significant cost savings in the long run, while also enhancing brand reputation and attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, sustainable industrial processes often involve the development of innovative technologies and materials. Investing in research and development for greener alternatives is essential for achieving significant improvements in environmental performance. This includes exploring alternative energy sources, developing more efficient manufacturing processes, and utilizing sustainable materials in product design. Companies that embrace these initiatives often gain a competitive edge in the market and demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility. Ultimately, the transition to sustainable industrial practices is not just about environmental protection, but also about economic and social advancement.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
A comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a critical component of any sustainable project. The EIA process involves identifying, predicting, evaluating, and mitigating the potential environmental impacts of a proposed action or development. This process is essential for making informed decisions and avoiding negative consequences. Thorough environmental assessments help stakeholders understand the potential ecological, social, and economic impacts before committing to a project. This proactive approach allows for the implementation of appropriate mitigation strategies, thereby minimizing any detrimental effects on the environment.
Effective mitigation strategies are key to minimizing negative environmental impacts. These strategies can range from implementing pollution control technologies to adopting alternative production methods. For instance, switching to renewable energy sources can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Careful planning and implementation of mitigation measures are crucial for minimizing the environmental footprint of industrial activities. This often involves collaboration between industries, government agencies, and environmental organizations to ensure comprehensive and effective solutions.
Successful environmental impact assessments and mitigation strategies are not just about compliance with regulations; they are also about fostering innovation and promoting sustainable development. They encourage the integration of environmental considerations into all stages of a project, from initial planning to final implementation. By proactively addressing potential environmental issues, we can create a more sustainable future for all.