Introduction to Sustainable Automotive Manufacturing
Sustainable Materials in Vehicle Production
A crucial aspect of sustainable automotive manufacturing involves the utilization of eco-friendly materials. Transitioning from traditional, resource-intensive materials like steel and aluminum to lighter, more sustainable alternatives like recycled plastics and bio-based composites is essential. This shift not only reduces the environmental footprint of manufacturing but also contributes to the overall lifecycle sustainability of the vehicle, minimizing its impact on landfills and reducing the need for virgin material extraction.
The use of recycled materials in the production process, such as incorporating recycled aluminum or steel into new components, is a significant step towards minimizing waste and conserving natural resources. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact of manufacturing but also fosters a circular economy, encouraging the reuse and repurposing of existing materials.
Optimizing Manufacturing Processes for Efficiency
Sustainable automotive manufacturing necessitates a shift towards more energy-efficient and resource-conserving production processes. This includes implementing lean manufacturing principles, optimizing energy consumption during various stages of production, and exploring alternative power sources for machinery. By minimizing energy waste and maximizing operational efficiency, manufacturers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener automotive industry.
Advanced technologies, such as 3D printing and automated assembly lines, can play a crucial role in streamlining production processes and minimizing material waste. These technologies allow for greater precision in component production, reducing the need for excessive material and optimizing the use of resources during assembly.
Reducing Emissions throughout the Supply Chain
Sustainable automotive manufacturing extends beyond the factory floor to encompass the entire supply chain. Minimizing emissions throughout the supply chain, from raw material extraction to transportation and distribution, is critical. This involves collaborating with suppliers to adopt sustainable practices, using eco-friendly transportation methods, and optimizing logistics to reduce fuel consumption. By addressing emissions at all stages, manufacturers can achieve a more holistic and impactful approach to sustainability.
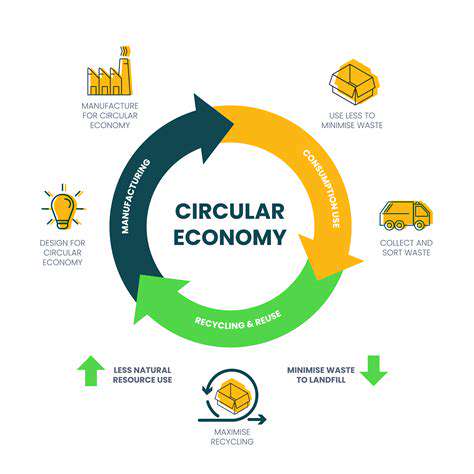
Promoting Circular Economy Principles
Embracing circular economy principles is paramount in sustainable automotive manufacturing. This involves designing vehicles for disassembly and reuse, maximizing the lifespan of components, and developing strategies for end-of-life vehicle management. By incorporating these principles, manufacturers can create a closed-loop system where materials are reused and recycled, minimizing waste and resource depletion. This approach fosters a more sustainable and environmentally conscious automotive industry, ensuring that vehicles contribute to a regenerative rather than a destructive system.

The Importance of Circular Economy Principles

A Paradigm Shift in Resource Management
The linear take-make-dispose model of resource management is increasingly unsustainable. It relies on finite resources and generates substantial waste, contributing to environmental degradation and economic instability. The circular economy, in contrast, aims to decouple economic growth from resource depletion. This paradigm shift emphasizes the importance of resource reuse, recycling, and regeneration, creating a closed-loop system where waste becomes a resource for new production.
This transition towards circularity requires a fundamental shift in mindset, from a focus on consumption to one that prioritizes sustainability and long-term value creation. This is not just an environmental imperative, but also an economic opportunity, generating new jobs and industries in the process.
Economic Benefits of Circularity
The circular economy offers substantial economic benefits. By reducing reliance on virgin materials and optimizing resource use, businesses can significantly lower production costs. This efficiency leads to increased profitability and competitiveness in the global market. Furthermore, circular models can stimulate innovation and the development of new technologies, creating new market opportunities and fostering economic growth. This is not just a theoretical concept; it's already producing tangible results in various industries.
The creation of new markets for recycled materials and the development of innovative reuse solutions foster a thriving circular economy ecosystem. This approach generates significant job opportunities, particularly in emerging sectors like recycling and refurbishment. The economic benefits are not only immediate, but also pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable future.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of the circular economy is profound. By minimizing waste generation and maximizing resource utilization, the circular economy drastically reduces pollution and environmental damage. This includes lowering greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, and protecting biodiversity. This approach significantly contributes to mitigating climate change and fostering a healthier planet for future generations. It's a crucial step towards a more sustainable future.
Implementing circular economy principles directly addresses the pressing environmental challenges of our time, from plastic pollution to deforestation. The reduction of waste and the preservation of natural resources are fundamental to maintaining the health of our planet and ensuring its long-term viability. This sustainability approach is not just a desirable goal, but a critical necessity.
Social Equity and Inclusivity
The circular economy's positive effects extend beyond the environment and the economy. It can contribute to social equity by creating opportunities for marginalized communities and fostering inclusive growth. This is achievable by providing access to resources and skills development in areas like recycling and reuse initiatives. The creation of new businesses and jobs can empower individuals and communities, leading to a more just and equitable society.
By creating and promoting sustainable business practices, the circular economy can foster a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities. This approach emphasizes social responsibility and ensures that the benefits of economic growth are shared widely. It is vital to incorporate social equity considerations in the design and implementation of circular economy strategies.